Product Description
1.Company Profile :
2.Specification :
|
CZPT CZPT spare parts Transmission shaft AZ |
|||
|
Type |
Transmission shaft |
Application |
Transmission shaft |
|
Truck model |
howo |
Certification |
ISO9001 |
|
OEM number |
AZ |
Warranty |
12 monthes |
|
Item Name |
Transmission shaft |
Packing |
standard |
|
Place of origin |
ZheJiang provice, china |
MOQ |
1 Piece |
|
Brand name |
CZPT |
Qulity |
OEM original |
|
Adaptable automobile mode: |
CZPT |
Payment |
TT, western union, L/C, paypal, etc. |
Propeller Shaft Product Introduction:
A propeller shaft, also known as a drive shaft or prop shaft, is a component used to transmit torque and rotation from the transmission to the drive wheels or propeller in a vehicle or vessel. It typically consists of a long metal shaft with universal joints on either end to allow for the flexing and movement of the suspension system.
Advantages of Propeller Shafts:
– Efficient transmission of power
– High load capacity and torque transmission capability
– Flexible and able to handle various angles and movements
– Durable and long-lasting with proper maintenance
– Consistent performance
Usage Range of Propeller Shafts:
– Automobiles (particularly rear-wheel or all-wheel-drive vehicles)
– Trucks and heavy duty vehicles
– Industrial machinery (such as pumps or generators)
– Marine vessels (such as boats and ships)
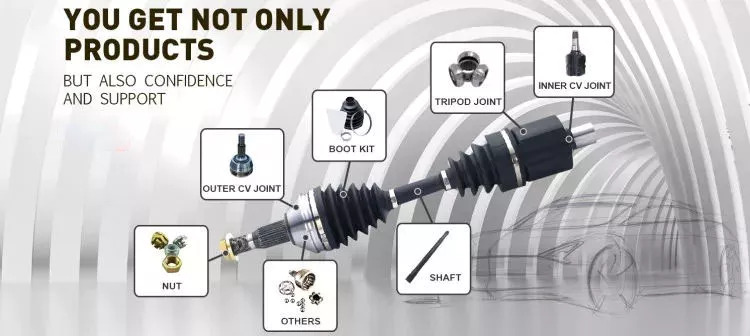
3.Picture shows
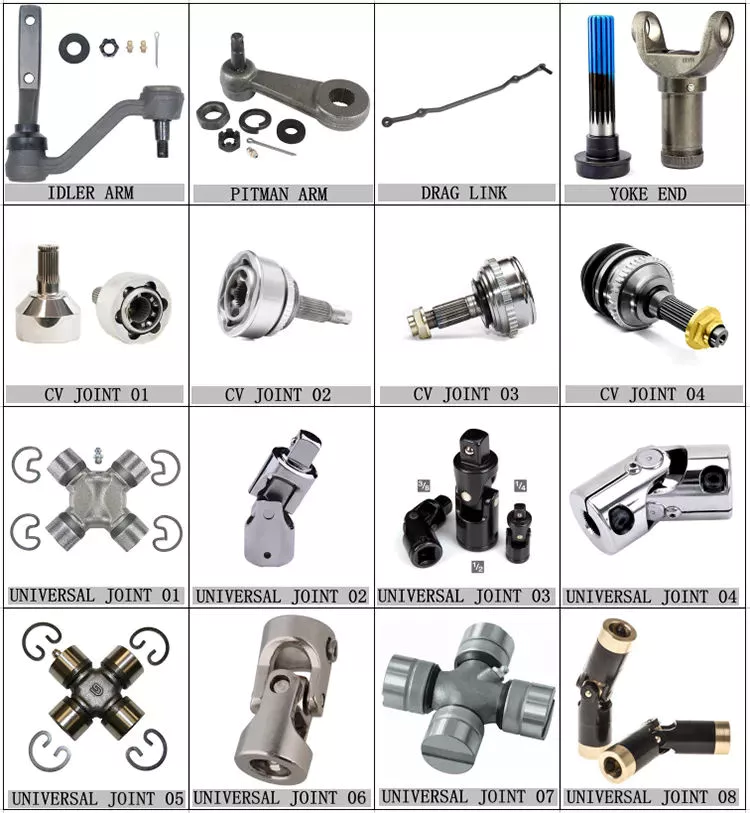
4.OTHER PARTS
5.WORK SHOP
6.Transport
7.Customer’s Voice
8.WHY CHOOSE US:
1.we have 14 years experience in the business of auto spare parts
2.good quality,reasonable lower price
3.fast delivery
4.with 24 hours online technical support
5.Sample will be offered before the trial order
Note: There are also kinds of products used for heavy truck for you to choose, if any need or interest, welcome to send us your detailed inquiry list.
/* May 10, 2571 16:49:51 */!function(){function d(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
How do drive shafts ensure efficient power transfer while maintaining balance?
Drive shafts employ various mechanisms to ensure efficient power transfer while maintaining balance. Efficient power transfer refers to the ability of the drive shaft to transmit rotational power from the source (such as an engine) to the driven components (such as wheels or machinery) with minimal energy loss. Balancing, on the other hand, involves minimizing vibrations and eliminating any uneven distribution of mass that can cause disturbances during operation. Here’s an explanation of how drive shafts achieve both efficient power transfer and balance:
1. Material Selection:
The material selection for drive shafts is crucial for maintaining balance and ensuring efficient power transfer. Drive shafts are commonly made from materials such as steel or aluminum alloys, chosen for their strength, stiffness, and durability. These materials have excellent dimensional stability and can withstand the torque loads encountered during operation. By using high-quality materials, drive shafts can minimize deformation, flexing, and imbalances that could compromise power transmission and generate vibrations.
2. Design Considerations:
The design of the drive shaft plays a significant role in both power transfer efficiency and balance. Drive shafts are engineered to have appropriate dimensions, including diameter and wall thickness, to handle the anticipated torque loads without excessive deflection or vibration. The design also considers factors such as the length of the drive shaft, the number and type of joints (such as universal joints or constant velocity joints), and the use of balancing weights. By carefully designing the drive shaft, manufacturers can achieve optimal power transfer efficiency while minimizing the potential for imbalance-induced vibrations.
3. Balancing Techniques:
Balance is crucial for drive shafts as any imbalance can cause vibrations, noise, and accelerated wear. To maintain balance, drive shafts undergo various balancing techniques during the manufacturing process. Static and dynamic balancing methods are employed to ensure that the mass distribution along the drive shaft is uniform. Static balancing involves adding counterweights at specific locations to offset any weight imbalances. Dynamic balancing is performed by spinning the drive shaft at high speeds and measuring any vibrations. If imbalances are detected, additional adjustments are made to achieve a balanced state. These balancing techniques help minimize vibrations and ensure smooth operation of the drive shaft.
4. Universal Joints and Constant Velocity Joints:
Drive shafts often incorporate universal joints (U-joints) or constant velocity (CV) joints to accommodate misalignment and maintain balance during operation. U-joints are flexible joints that allow for angular movement between shafts. They are typically used in applications where the drive shaft operates at varying angles. CV joints, on the other hand, are designed to maintain a constant velocity of rotation and are commonly used in front-wheel-drive vehicles. By incorporating these joints, drive shafts can compensate for misalignment, reduce stress on the shaft, and minimize vibrations that can negatively impact power transfer efficiency and balance.
5. Maintenance and Inspection:
Regular maintenance and inspection of drive shafts are essential for ensuring efficient power transfer and balance. Periodic checks for wear, damage, or misalignment can help identify any issues that may affect the drive shaft’s performance. Lubrication of the joints and proper tightening of fasteners are also critical for maintaining optimal operation. By adhering to recommended maintenance procedures, any imbalances or inefficiencies can be addressed promptly, ensuring continued efficient power transfer and balance.
In summary, drive shafts ensure efficient power transfer while maintaining balance through careful material selection, thoughtful design considerations, balancing techniques, and the incorporation of flexible joints. By optimizing these factors, drive shafts can transmit rotational power smoothly and reliably, minimizing energy losses and vibrations that can impact performance and longevity.

Can drive shafts be customized for specific vehicle or equipment requirements?
Yes, drive shafts can be customized to meet specific vehicle or equipment requirements. Customization allows manufacturers to tailor the design, dimensions, materials, and other parameters of the drive shaft to ensure compatibility and optimal performance within a particular vehicle or equipment. Here’s a detailed explanation of how drive shafts can be customized:
1. Dimensional Customization:
Drive shafts can be customized to match the dimensional requirements of the vehicle or equipment. This includes adjusting the overall length, diameter, and spline configuration to ensure proper fitment and clearances within the specific application. By customizing the dimensions, the drive shaft can be seamlessly integrated into the driveline system without any interference or limitations.
2. Material Selection:
The choice of materials for drive shafts can be customized based on the specific requirements of the vehicle or equipment. Different materials, such as steel alloys, aluminum alloys, or specialized composites, can be selected to optimize strength, weight, and durability. The material selection can be tailored to meet the torque, speed, and operating conditions of the application, ensuring the drive shaft’s reliability and longevity.
3. Joint Configuration:
Drive shafts can be customized with different joint configurations to accommodate specific vehicle or equipment requirements. For example, universal joints (U-joints) may be suitable for applications with lower operating angles and moderate torque demands, while constant velocity (CV) joints are often used in applications requiring higher operating angles and smoother power transmission. The choice of joint configuration depends on factors such as operating angle, torque capacity, and desired performance characteristics.
4. Torque and Power Capacity:
Customization allows drive shafts to be designed with the appropriate torque and power capacity for the specific vehicle or equipment. Manufacturers can analyze the torque requirements, operating conditions, and safety margins of the application to determine the optimal torque rating and power capacity of the drive shaft. This ensures that the drive shaft can handle the required loads without experiencing premature failure or performance issues.
5. Balancing and Vibration Control:
Drive shafts can be customized with precision balancing and vibration control measures. Imbalances in the drive shaft can lead to vibrations, increased wear, and potential driveline issues. By employing dynamic balancing techniques during the manufacturing process, manufacturers can minimize vibrations and ensure smooth operation. Additionally, vibration dampers or isolation systems can be integrated into the drive shaft design to further mitigate vibrations and enhance overall system performance.
6. Integration and Mounting Considerations:
Customization of drive shafts takes into account the integration and mounting requirements of the specific vehicle or equipment. Manufacturers work closely with the vehicle or equipment designers to ensure that the drive shaft fits seamlessly into the driveline system. This includes adapting the mounting points, interfaces, and clearances to ensure proper alignment and installation of the drive shaft within the vehicle or equipment.
7. Collaboration and Feedback:
Manufacturers often collaborate with vehicle manufacturers, OEMs (Original Equipment Manufacturers), or end-users to gather feedback and incorporate their specific requirements into the drive shaft customization process. By actively seeking input and feedback, manufacturers can address specific needs, optimize performance, and ensure compatibility with the vehicle or equipment. This collaborative approach enhances the customization process and results in drive shafts that meet the exact requirements of the application.
8. Compliance with Standards:
Customized drive shafts can be designed to comply with relevant industry standards and regulations. Compliance with standards, such as ISO (International Organization for Standardization) or specific industry standards, ensures that the customized drive shafts meet quality, safety, and performance requirements. Adhering to these standards provides assurance that the drive shafts are compatible and can be seamlessly integrated into the specific vehicle or equipment.
In summary, drive shafts can be customized to meet specific vehicle or equipment requirements through dimensional customization, material selection, joint configuration, torque and power capacity optimization, balancing and vibration control, integration and mounting considerations, collaboration with stakeholders, and compliance with industry standards. Customization allows drive shafts to be precisely tailored to the needs of the application, ensuring compatibility, reliability, and optimal performance.

What benefits do drive shafts offer for different types of vehicles and equipment?
Drive shafts offer several benefits for different types of vehicles and equipment. They play a crucial role in power transmission and contribute to the overall performance, efficiency, and functionality of various systems. Here’s a detailed explanation of the benefits that drive shafts provide:
1. Efficient Power Transmission:
Drive shafts enable efficient power transmission from the engine or power source to the wheels or driven components. By connecting the engine or motor to the driven system, drive shafts efficiently transfer rotational power, allowing vehicles and equipment to perform their intended functions. This efficient power transmission ensures that the power generated by the engine is effectively utilized, optimizing the overall performance and productivity of the system.
2. Versatility:
Drive shafts offer versatility in their applications. They are used in various types of vehicles, including cars, trucks, motorcycles, and off-road vehicles. Additionally, drive shafts are employed in a wide range of equipment and machinery, such as agricultural machinery, construction equipment, industrial machinery, and marine vessels. The ability to adapt to different types of vehicles and equipment makes drive shafts a versatile component for power transmission.
3. Torque Handling:
Drive shafts are designed to handle high levels of torque. Torque is the rotational force generated by the engine or power source. Drive shafts are engineered to efficiently transmit this torque without excessive twisting or bending. By effectively handling torque, drive shafts ensure that the power generated by the engine is reliably transferred to the wheels or driven components, enabling vehicles and equipment to overcome resistance, such as heavy loads or challenging terrains.
4. Flexibility and Compensation:
Drive shafts provide flexibility and compensation for angular movement and misalignment. In vehicles, drive shafts accommodate the movement of the suspension system, allowing the wheels to move up and down independently. This flexibility ensures a constant power transfer even when the vehicle encounters uneven terrain. Similarly, in machinery, drive shafts compensate for misalignment between the engine or motor and the driven components, ensuring smooth power transmission and preventing excessive stress on the drivetrain.
5. Weight Reduction:
Drive shafts contribute to weight reduction in vehicles and equipment. Compared to other forms of power transmission, such as belt drives or chain drives, drive shafts are typically lighter in weight. This reduction in weight helps improve fuel efficiency in vehicles and reduces the overall weight of equipment, leading to enhanced maneuverability and increased payload capacity. Additionally, lighter drive shafts contribute to a better power-to-weight ratio, resulting in improved performance and acceleration.
6. Durability and Longevity:
Drive shafts are designed to be durable and long-lasting. They are constructed using materials such as steel or aluminum, which offer high strength and resistance to wear and fatigue. Drive shafts undergo rigorous testing and quality control measures to ensure their reliability and longevity. Proper maintenance, including lubrication and regular inspections, further enhances their durability. The robust construction and long lifespan of drive shafts contribute to the overall reliability and cost-effectiveness of vehicles and equipment.
7. Safety:
Drive shafts incorporate safety features to protect operators and bystanders. In vehicles, drive shafts are often enclosed within a protective tube or housing, preventing contact with moving parts and reducing the risk of injury in the event of a failure. Similarly, in machinery, safety shields or guards are commonly installed around exposed drive shafts to minimize the potential hazards associated with rotating components. These safety measures ensure the well-being of individuals operating or working in proximity to vehicles and equipment.
In summary, drive shafts offer several benefits for different types of vehicles and equipment. They enable efficient power transmission, provide versatility in various applications, handle torque effectively, offer flexibility and compensation, contribute to weight reduction, ensure durability and longevity, and incorporate safety features. By providing these advantages, drive shafts enhance the performance, efficiency, reliability, and safety of vehicles and equipment across a wide range of industries.


editor by lmc 2024-11-19
China Custom Applicable to Porsche Panamera Drive Shaft 970 Series 97042101102 97042101104 Panamera Drive Shaft Universal Joint Disc Ball Cage Dust Cover Bearing
Product Description
| OE | 9757101104 |
| Vehicle model | Panamera 970 |
We are committed to the production and research and development of transmission shafts, as well as the sales of mid to high-end automotive transmission shafts. We serve high-quality customers with high-quality products. At present, we mainly produce Mercedes Benz, BMW, Audi, Volkswagen, Porsche, Volvo, Land Rover, Jaguar, Maserati, Ferrari, Lamborghini, and Bentley
Reasons for choosing us
1. High quality (quieter to move)
2. After sales worry free (one-on-1 service)
3. Factory direct sales (bypassing intermediaries)
4. Support for 1 custom thread
/* May 10, 2571 16:49:51 */!function(){function d(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1

Are there any limitations or disadvantages associated with drive shafts?
While drive shafts are widely used and offer several advantages, they also have certain limitations and disadvantages that should be considered. Here’s a detailed explanation of the limitations and disadvantages associated with drive shafts:
1. Length and Misalignment Constraints:
Drive shafts have a maximum practical length due to factors such as material strength, weight considerations, and the need to maintain rigidity and minimize vibrations. Longer drive shafts can be prone to increased bending and torsional deflection, leading to reduced efficiency and potential driveline vibrations. Additionally, drive shafts require proper alignment between the driving and driven components. Misalignment can cause increased wear, vibrations, and premature failure of the drive shaft or its associated components.
2. Limited Operating Angles:
Drive shafts, especially those using U-joints, have limitations on operating angles. U-joints are typically designed to operate within specific angular ranges, and operating beyond these limits can result in reduced efficiency, increased vibrations, and accelerated wear. In applications requiring large operating angles, constant velocity (CV) joints are often used to maintain a constant speed and accommodate greater angles. However, CV joints may introduce higher complexity and cost compared to U-joints.
3. Maintenance Requirements:
Drive shafts require regular maintenance to ensure optimal performance and reliability. This includes periodic inspection, lubrication of joints, and balancing if necessary. Failure to perform routine maintenance can lead to increased wear, vibrations, and potential driveline issues. Maintenance requirements should be considered in terms of time and resources when using drive shafts in various applications.
4. Noise and Vibration:
Drive shafts can generate noise and vibrations, especially at high speeds or when operating at certain resonant frequencies. Imbalances, misalignment, worn joints, or other factors can contribute to increased noise and vibrations. These vibrations may affect the comfort of vehicle occupants, contribute to component fatigue, and require additional measures such as dampers or vibration isolation systems to mitigate their effects.
5. Weight and Space Constraints:
Drive shafts add weight to the overall system, which can be a consideration in weight-sensitive applications, such as automotive or aerospace industries. Additionally, drive shafts require physical space for installation. In compact or tightly packaged equipment or vehicles, accommodating the necessary drive shaft length and clearances can be challenging, requiring careful design and integration considerations.
6. Cost Considerations:
Drive shafts, depending on their design, materials, and manufacturing processes, can involve significant costs. Customized or specialized drive shafts tailored to specific equipment requirements may incur higher expenses. Additionally, incorporating advanced joint configurations, such as CV joints, can add complexity and cost to the drive shaft system.
7. Inherent Power Loss:
Drive shafts transmit power from the driving source to the driven components, but they also introduce some inherent power loss due to friction, bending, and other factors. This power loss can reduce overall system efficiency, particularly in long drive shafts or applications with high torque requirements. It is important to consider power loss when determining the appropriate drive shaft design and specifications.
8. Limited Torque Capacity:
While drive shafts can handle a wide range of torque loads, there are limits to their torque capacity. Exceeding the maximum torque capacity of a drive shaft can lead to premature failure, resulting in downtime and potential damage to other driveline components. It is crucial to select a drive shaft with sufficient torque capacity for the intended application.
Despite these limitations and disadvantages, drive shafts remain a widely used and effective means of power transmission in various industries. Manufacturers continuously work to address these limitations through advancements in materials, design techniques, joint configurations, and balancing processes. By carefully considering the specific application requirements and potential drawbacks, engineers and designers can mitigate the limitations and maximize the benefits of drive shafts in their respective systems.

What safety precautions should be followed when working with drive shafts?
Working with drive shafts requires adherence to specific safety precautions to prevent accidents, injuries, and damage to equipment. Drive shafts are critical components of a vehicle or machinery’s driveline system and can pose hazards if not handled properly. Here’s a detailed explanation of the safety precautions that should be followed when working with drive shafts:
1. Personal Protective Equipment (PPE):
Always wear appropriate personal protective equipment when working with drive shafts. This may include safety goggles, gloves, steel-toed boots, and protective clothing. PPE helps protect against potential injuries from flying debris, sharp edges, or accidental contact with moving parts.
2. Lockout/Tagout Procedures:
Before working on a drive shaft, ensure that the power source is properly locked out and tagged out. This involves isolating the power supply, such as shutting off the engine or disconnecting the electrical power, and securing it with a lockout/tagout device. This prevents accidental engagement of the drive shaft while maintenance or repair work is being performed.
3. Vehicle or Equipment Support:
When working with drive shafts in vehicles or equipment, use proper support mechanisms to prevent unexpected movement. Securely block the vehicle’s wheels or utilize support stands to prevent the vehicle from rolling or shifting during drive shaft removal or installation. This helps maintain stability and reduces the risk of accidents.
4. Proper Lifting Techniques:
When handling heavy drive shafts, use proper lifting techniques to prevent strain or injuries. Lift with the help of a suitable lifting device, such as a hoist or jack, and ensure that the load is evenly distributed and securely attached. Avoid lifting heavy drive shafts manually or with improper lifting equipment, as this can lead to accidents and injuries.
5. Inspection and Maintenance:
Prior to working on a drive shaft, thoroughly inspect it for any signs of damage, wear, or misalignment. If any abnormalities are detected, consult a qualified technician or engineer before proceeding. Regular maintenance is also essential to ensure the drive shaft is in good working condition. Follow the manufacturer’s recommended maintenance schedule and procedures to minimize the risk of failures or malfunctions.
6. Proper Tools and Equipment:
Use appropriate tools and equipment specifically designed for working with drive shafts. Improper tools or makeshift solutions can lead to accidents or damage to the drive shaft. Ensure that tools are in good condition, properly sized, and suitable for the task at hand. Follow the manufacturer’s instructions and guidelines when using specialized tools or equipment.
7. Controlled Release of Stored Energy:
Some drive shafts, particularly those with torsional dampers or other energy-storing components, can store energy even when the power source is disconnected. Exercise caution when working on such drive shafts and ensure that the stored energy is safely released before disassembly or removal.
8. Training and Expertise:
Work on drive shafts should only be performed by individuals with the necessary training, knowledge, and expertise. If you are not familiar with drive shafts or lack the required skills, seek assistance from qualified technicians or professionals. Improper handling or installation of drive shafts can lead to accidents, damage, or compromised performance.
9. Follow Manufacturer’s Guidelines:
Always follow the manufacturer’s guidelines, instructions, and warnings specific to the drive shaft you are working with. These guidelines provide important information regarding installation, maintenance, and safety considerations. Deviating from the manufacturer’s recommendations may result in unsafe conditions or void warranty coverage.
10. Disposal of Old or Damaged Drive Shafts:
Dispose of old or damaged drive shafts in accordance with local regulations and environmental guidelines. Improper disposal can have negative environmental impacts and may violate legal requirements. Consult with local waste management authorities or recycling centers to ensure appropriate disposal methods are followed.
By following these safety precautions, individuals can minimize the risks associated with working with drive shafts and promote a safe working environment. It is crucial to prioritize personal safety, use proper equipment and techniques, and seek professional help when needed to ensure the proper handling and maintenance of drive shafts.

What benefits do drive shafts offer for different types of vehicles and equipment?
Drive shafts offer several benefits for different types of vehicles and equipment. They play a crucial role in power transmission and contribute to the overall performance, efficiency, and functionality of various systems. Here’s a detailed explanation of the benefits that drive shafts provide:
1. Efficient Power Transmission:
Drive shafts enable efficient power transmission from the engine or power source to the wheels or driven components. By connecting the engine or motor to the driven system, drive shafts efficiently transfer rotational power, allowing vehicles and equipment to perform their intended functions. This efficient power transmission ensures that the power generated by the engine is effectively utilized, optimizing the overall performance and productivity of the system.
2. Versatility:
Drive shafts offer versatility in their applications. They are used in various types of vehicles, including cars, trucks, motorcycles, and off-road vehicles. Additionally, drive shafts are employed in a wide range of equipment and machinery, such as agricultural machinery, construction equipment, industrial machinery, and marine vessels. The ability to adapt to different types of vehicles and equipment makes drive shafts a versatile component for power transmission.
3. Torque Handling:
Drive shafts are designed to handle high levels of torque. Torque is the rotational force generated by the engine or power source. Drive shafts are engineered to efficiently transmit this torque without excessive twisting or bending. By effectively handling torque, drive shafts ensure that the power generated by the engine is reliably transferred to the wheels or driven components, enabling vehicles and equipment to overcome resistance, such as heavy loads or challenging terrains.
4. Flexibility and Compensation:
Drive shafts provide flexibility and compensation for angular movement and misalignment. In vehicles, drive shafts accommodate the movement of the suspension system, allowing the wheels to move up and down independently. This flexibility ensures a constant power transfer even when the vehicle encounters uneven terrain. Similarly, in machinery, drive shafts compensate for misalignment between the engine or motor and the driven components, ensuring smooth power transmission and preventing excessive stress on the drivetrain.
5. Weight Reduction:
Drive shafts contribute to weight reduction in vehicles and equipment. Compared to other forms of power transmission, such as belt drives or chain drives, drive shafts are typically lighter in weight. This reduction in weight helps improve fuel efficiency in vehicles and reduces the overall weight of equipment, leading to enhanced maneuverability and increased payload capacity. Additionally, lighter drive shafts contribute to a better power-to-weight ratio, resulting in improved performance and acceleration.
6. Durability and Longevity:
Drive shafts are designed to be durable and long-lasting. They are constructed using materials such as steel or aluminum, which offer high strength and resistance to wear and fatigue. Drive shafts undergo rigorous testing and quality control measures to ensure their reliability and longevity. Proper maintenance, including lubrication and regular inspections, further enhances their durability. The robust construction and long lifespan of drive shafts contribute to the overall reliability and cost-effectiveness of vehicles and equipment.
7. Safety:
Drive shafts incorporate safety features to protect operators and bystanders. In vehicles, drive shafts are often enclosed within a protective tube or housing, preventing contact with moving parts and reducing the risk of injury in the event of a failure. Similarly, in machinery, safety shields or guards are commonly installed around exposed drive shafts to minimize the potential hazards associated with rotating components. These safety measures ensure the well-being of individuals operating or working in proximity to vehicles and equipment.
In summary, drive shafts offer several benefits for different types of vehicles and equipment. They enable efficient power transmission, provide versatility in various applications, handle torque effectively, offer flexibility and compensation, contribute to weight reduction, ensure durability and longevity, and incorporate safety features. By providing these advantages, drive shafts enhance the performance, efficiency, reliability, and safety of vehicles and equipment across a wide range of industries.


editor by lmc 2024-11-08
China Good quality 37100-04342 for CHINAMFG Tacoma 07-14 Propshaft Tail Shaft Drive Shaft Manufacturer
Product Description
As a professional manufacturer for propeller shaft, we have +800 items for all kinds of car, main suitable
for AMERICA & EUROPE market.
Our advantage:
1. Full range of products
2. MOQ qty: 5pcs/items
3. Delivery on time
4: Warranty: 1 YEAR
5. Develope new items: FREE
| OEM NO. | 65-5012 37100-5712 936-724 |
| Application | for CZPT Tacoma 07-14 |
| Material | SS430/45# steel |
| Balancing Standrad | G16, 3200rpm |
| Warranty | One Year |
For some items, we have stock, small order (+3000USD) is welcome.
The following items are some of propeller shafts for Toyota, If you need more information, pls contact us for ASAP.
|
Propeller Shaft for TOYOTA |
|||
|
OEM |
Application |
OEM |
Application |
| 37302-20040 | for TOYOTA | 37110-65710 | for CZPT Land Cruiser 77-80 |
| 37120-0K030 | for TOYOTA | 37110-65710 | for CZPT Land Cruiser 81-85 |
| 37120-30420 | for TOYOTA | 37140-60170 | for CZPT Land Cruiser 85-87 |
| 37140-6571 | for TOYOTA | 37140-65710 | for CZPT Land Cruiser 88-90 |
| 37140-35050 | for TOYOTA | 37140-6 0571 | for CZPT Land Cruiser 90-06 |
| 37140-60480 | for CZPT 4Runner 03-09 | 37140-60540 | for CZPT Land Cruiser 90-07 |
| 37110-6A440 | for CZPT 4Runner 03-09 | 37110-60450 | for CZPT Land Cruiser 90-92 |
| 37140-60380 | for CZPT 4Runner 10-18 | 37110-6571 | for CZPT Land Cruiser 90-99 |
| 37140-35060 | for CZPT 4Runner 88-95 | 37140-65710 | for CZPT Land Cruiser 90-99 |
| 65-9919 | for CZPT 4Runner 89-95 | 37110-60460 | for CZPT Land Cruiser 91-97 |
| 37140-35090 | for CZPT 4Runner 89-95 | 37110-60520 | for CZPT Land Cruiser 92-97 |
| 37140-35071 | for CZPT 4Runner 90-92 | 37110-6A620 | for CZPT Land Cruiser 98-07 |
| 37140-35130 | for CZPT 4Runner 96-00 | 37110-6A250 | for CZPT Land Cruiser 99-00 |
| 936-711 | for CZPT 4Runner 96-02 | 37110-6A310 | for CZPT Land Crusier |
| 37110-6571 | for CZPT 4Runner 96-20 | 37110-6A610 | for CZPT Land Crusier 98-02 |
| 37110-3D300 | for CZPT 4Runner 96-20 | 65-9375 | for CZPT Pickup 79-83 |
| 37110-3D060 | for CZPT 4Runner 97-02 | 37140-35013 | for CZPT Pickup 80-83 |
| 37140-35190 | for CZPT 4Runner 99-02 | 65-9376 | for CZPT Pickup 84-87 |
| 37120-30390 | for CZPT Crown | 65-9842 | for CZPT Previa 91-97 |
| 37100-48571 | for CZPT Highlander 01-07 | 37100-42060 | for CZPT RAV4 01-05 |
| 37100-48030 | for CZPT Highlander 08-14 | 37100-42090 | for CZPT RAV4 06-16 |
| 37110-60A20 | for CZPT Hilux | 37110-34120 | for CZPT Sequoia 07 |
| 37140-0K571 | for CZPT Hilux | 37100-45571 | for CZPT Sienna 04-10 |
| 37100-0K181 | for CZPT Hilux | 37100-45571 | for CZPT SIENNA 2011-2018 |
| 37140-0K030 | for CZPT Hilux 05-11 | 936-728 | for CZPT Tacoma 05-15 |
| 37100-0K091 | for CZPT Hilux 05-15 | 37100-5712 | for CZPT Tacoma 07-14 |
| 37100-0K081 | for CZPT Hilux 05-15 | 936-708 | for CZPT Tacoma 2.7L 99-04 |
| 37100-0K480 | for CZPT Hilux 2571 | 37100-35750 | for CZPT Tacoma 2004 |
| 37140-35030 | for CZPT Hilux 93-95 | 37100-5712 | for CZPT Tacoma 2011-2015 |
| 37100-0K030 | for CZPT Hilux 05- | 936-738 | for CZPT Tacoma 4.0L 05-15 |
| 37110-60330 | for CZPT HJ60 82-84 | 37100-3D240 | for CZPT Tacoma 95-04 |
| 371002A190 | for CZPT JZX100 96-00 | 37140-35180 | for CZPT Tacoma 95-04 |
| 37140-60121 | for CZPT Land Cruiser | 37100-35820 | for CZPT Tacoma 95-99 |
| 37140-65710 | for CZPT Land Cruiser | 37100-3D250 | for CZPT Tacoma 98-04 |
| 37140-65710 | for CZPT Land Cruiser | 37100-3D260 | for CZPT Tacoma 99-04 |
| 37140-60320 | for CZPT Land Cruiser | 936-717 | for CZPT Tundra 04 |
| 37140-60330 | for CZPT Land Cruiser | 37100-34130 | for CZPT Tundra 05-06 |
| 37140-6571 | for CZPT Land Cruiser | 65-9257 | for CZPT Tundra 2001-2004 |
| 37140-60430 | for CZPT Land Cruiser | 37100-34120 | for CZPT Tundra 4.7L 05-06 |
| 37140-60450 | for CZPT Land Cruiser | 37110-6A430 | for CZPT Land Cruiser 00-02 |
| 37140-6A610 | for CZPT Land Cruiser | 37140-6571 | for CZPT Land Cruiser 02-09 |
| 37140-60080 | for CZPT Land Cruiser | 37110-60A50 | for CZPT Land Cruiser 07 |
| 37110-60620 | for CZPT Land Cruiser | 37140-60590 | for CZPT Land Cruiser 08-15 |
| 37110-6A260 | for CZPT Land Cruiser | 37140-60090 | for CZPT Land Cruiser 74-80 |
/* May 10, 2571 16:49:51 */!function(){function d(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1

How do drive shafts handle variations in speed and torque during operation?
Drive shafts are designed to handle variations in speed and torque during operation by employing specific mechanisms and configurations. These mechanisms allow the drive shafts to accommodate the changing demands of power transmission while maintaining smooth and efficient operation. Here’s a detailed explanation of how drive shafts handle variations in speed and torque:
1. Flexible Couplings:
Drive shafts often incorporate flexible couplings, such as universal joints (U-joints) or constant velocity (CV) joints, to handle variations in speed and torque. These couplings provide flexibility and allow the drive shaft to transmit power even when the driving and driven components are not perfectly aligned. U-joints consist of two yokes connected by a cross-shaped bearing, allowing for angular movement between the drive shaft sections. This flexibility accommodates variations in speed and torque and compensates for misalignment. CV joints, which are commonly used in automotive drive shafts, maintain a constant velocity of rotation while accommodating changing operating angles. These flexible couplings enable smooth power transmission and reduce vibrations and wear caused by speed and torque variations.
2. Slip Joints:
In some drive shaft designs, slip joints are incorporated to handle variations in length and accommodate changes in distance between the driving and driven components. A slip joint consists of an inner and outer tubular section with splines or a telescoping mechanism. As the drive shaft experiences changes in length due to suspension movement or other factors, the slip joint allows the shaft to extend or compress without affecting the power transmission. By allowing axial movement, slip joints help prevent binding or excessive stress on the drive shaft during variations in speed and torque, ensuring smooth operation.
3. Balancing:
Drive shafts undergo balancing procedures to optimize their performance and minimize vibrations caused by speed and torque variations. Imbalances in the drive shaft can lead to vibrations, which not only affect the comfort of vehicle occupants but also increase wear and tear on the shaft and its associated components. Balancing involves redistributing mass along the drive shaft to achieve even weight distribution, reducing vibrations and improving overall performance. Dynamic balancing, which typically involves adding or removing small weights, ensures that the drive shaft operates smoothly even under varying speeds and torque loads.
4. Material Selection and Design:
The selection of materials and the design of drive shafts play a crucial role in handling variations in speed and torque. Drive shafts are typically made from high-strength materials, such as steel or aluminum alloys, chosen for their ability to withstand the forces and stresses associated with varying operating conditions. The diameter and wall thickness of the drive shaft are also carefully determined to ensure sufficient strength and stiffness. Additionally, the design incorporates considerations for factors such as critical speed, torsional rigidity, and resonance avoidance, which help maintain stability and performance during speed and torque variations.
5. Lubrication:
Proper lubrication is essential for drive shafts to handle variations in speed and torque. Lubricating the joints, such as U-joints or CV joints, reduces friction and heat generated during operation, ensuring smooth movement and minimizing wear. Adequate lubrication also helps prevent the binding of components, allowing the drive shaft to accommodate speed and torque variations more effectively. Regular lubrication maintenance is necessary to ensure optimal performance and extend the lifespan of the drive shaft.
6. System Monitoring:
Monitoring the performance of the drive shaft system is important to identify any issues related to variations in speed and torque. Unusual vibrations, noises, or changes in power transmission can indicate potential problems with the drive shaft. Regular inspections and maintenance checks allow for the early detection and resolution of issues, helping to prevent further damage and ensure the drive shaft continues to handle speed and torque variations effectively.
In summary, drive shafts handle variations in speed and torque during operation through the use of flexible couplings, slip joints, balancing procedures, appropriate material selection and design, lubrication, and system monitoring. These mechanisms and practices allow the drive shaft to accommodate misalignment, changes in length, and variations in power demands, ensuring efficient power transmission, smooth operation, and reduced wear and tear in various applications.

Can you provide real-world examples of vehicles and machinery that use drive shafts?
Drive shafts are widely used in various vehicles and machinery to transmit power from the engine or power source to the wheels or driven components. Here are some real-world examples of vehicles and machinery that utilize drive shafts:
1. Automobiles:
Drive shafts are commonly found in automobiles, especially those with rear-wheel drive or four-wheel drive systems. In these vehicles, the drive shaft transfers power from the transmission or transfer case to the rear differential or front differential, respectively. This allows the engine’s power to be distributed to the wheels, propelling the vehicle forward.
2. Trucks and Commercial Vehicles:
Drive shafts are essential components in trucks and commercial vehicles. They are used to transfer power from the transmission or transfer case to the rear axle or multiple axles in the case of heavy-duty trucks. Drive shafts in commercial vehicles are designed to handle higher torque loads and are often larger and more robust than those used in passenger cars.
3. Construction and Earthmoving Equipment:
Various types of construction and earthmoving equipment, such as excavators, loaders, bulldozers, and graders, rely on drive shafts for power transmission. These machines typically have complex drivetrain systems that use drive shafts to transfer power from the engine to the wheels or tracks, enabling them to perform heavy-duty tasks on construction sites or in mining operations.
4. Agricultural Machinery:
Agricultural machinery, including tractors, combines, and harvesters, utilize drive shafts to transmit power from the engine to the wheels or driven components. Drive shafts in agricultural machinery are often subjected to demanding conditions and may have additional features such as telescopic sections to accommodate variable distances between components.
5. Industrial Machinery:
Industrial machinery, such as manufacturing equipment, generators, pumps, and compressors, often incorporate drive shafts in their power transmission systems. These drive shafts transfer power from electric motors, engines, or other power sources to various driven components, enabling the machinery to perform specific tasks in industrial settings.
6. Marine Vessels:
In marine applications, drive shafts are commonly used to transmit power from the engine to the propeller in boats, ships, and other watercraft. Marine drive shafts are typically longer and designed to withstand the unique challenges posed by water environments, including corrosion resistance and appropriate sealing mechanisms.
7. Recreational Vehicles (RVs) and Motorhomes:
RVs and motorhomes often employ drive shafts as part of their drivetrain systems. These drive shafts transfer power from the transmission to the rear axle, allowing the vehicle to move and providing propulsion. Drive shafts in RVs may have additional features such as dampers or vibration-reducing components to enhance comfort during travel.
8. Off-Road and Racing Vehicles:
Off-road vehicles, such as SUVs, trucks, and all-terrain vehicles (ATVs), as well as racing vehicles, frequently utilize drive shafts. These drive shafts are designed to withstand the rigors of off-road conditions or high-performance racing, transmitting power efficiently to the wheels and ensuring optimal traction and performance.
9. Railway Rolling Stock:
In railway systems, drive shafts are employed in locomotives and some types of rolling stock. They transfer power from the locomotive’s engine to the wheels or propulsion system, enabling the train to move along the tracks. Railway drive shafts are typically much longer and may have additional features to accommodate the articulated or flexible nature of some train configurations.
10. Wind Turbines:
Large-scale wind turbines used for generating electricity incorporate drive shafts in their power transmission systems. The drive shafts transfer rotational energy from the turbine’s blades to the generator, where it is converted into electrical power. Drive shafts in wind turbines are designed to handle the significant torque and rotational forces generated by the wind.
These examples demonstrate the broad range of vehicles and machinery that rely on drive shafts for efficient power transmission and propulsion. Drive shafts are essential components in various industries, enabling the transfer of power from the source to the driven components, ultimately facilitating movement, operation, or the performance of specific tasks.

What is a drive shaft and how does it function in vehicles and machinery?
A drive shaft, also known as a propeller shaft or prop shaft, is a mechanical component that plays a critical role in transmitting rotational power from the engine to the wheels or other driven components in vehicles and machinery. It is commonly used in various types of vehicles, including cars, trucks, motorcycles, and agricultural or industrial machinery. Here’s a detailed explanation of what a drive shaft is and how it functions:
1. Definition and Construction: A drive shaft is a cylindrical metal tube that connects the engine or power source to the wheels or driven components. It is typically made of steel or aluminum and consists of one or more tubular sections with universal joints (U-joints) at each end. These U-joints allow for angular movement and compensation of misalignment between the engine/transmission and the driven wheels or components.
2. Power Transmission: The primary function of a drive shaft is to transmit rotational power from the engine or power source to the wheels or driven components. In vehicles, the drive shaft connects the transmission or gearbox output shaft to the differential, which then transfers power to the wheels. In machinery, the drive shaft transfers power from the engine or motor to various driven components such as pumps, generators, or other mechanical systems.
3. Torque and Speed: The drive shaft is responsible for transmitting both torque and rotational speed. Torque is the rotational force generated by the engine or power source, while rotational speed is the number of revolutions per minute (RPM). The drive shaft must be capable of transmitting the required torque without excessive twisting or bending and maintaining the desired rotational speed for efficient operation of the driven components.
4. Flexible Coupling: The U-joints on the drive shaft provide a flexible coupling that allows for angular movement and compensation of misalignment between the engine/transmission and the driven wheels or components. As the suspension system of a vehicle moves or the machinery operates on uneven terrain, the drive shaft can adjust its length and angle to accommodate these movements, ensuring smooth power transmission and preventing damage to the drivetrain components.
5. Length and Balance: The length of the drive shaft is determined by the distance between the engine or power source and the driven wheels or components. It should be appropriately sized to ensure proper power transmission and avoid excessive vibrations or bending. Additionally, the drive shaft is carefully balanced to minimize vibrations and rotational imbalances, which can cause discomfort, reduce efficiency, and lead to premature wear of drivetrain components.
6. Safety Considerations: Drive shafts in vehicles and machinery require proper safety measures. In vehicles, drive shafts are often enclosed within a protective tube or housing to prevent contact with moving parts and reduce the risk of injury in the event of a malfunction or failure. Additionally, safety shields or guards are commonly installed around exposed drive shafts in machinery to protect operators from potential hazards associated with rotating components.
7. Maintenance and Inspection: Regular maintenance and inspection of drive shafts are essential to ensure their proper functioning and longevity. This includes checking for signs of wear, damage, or excessive play in the U-joints, inspecting the drive shaft for any cracks or deformations, and lubricating the U-joints as recommended by the manufacturer. Proper maintenance helps prevent failures, ensures optimal performance, and prolongs the service life of the drive shaft.
In summary, a drive shaft is a mechanical component that transmits rotational power from the engine or power source to the wheels or driven components in vehicles and machinery. It functions by providing a rigid connection between the engine/transmission and the driven wheels or components, while also allowing for angular movement and compensation of misalignment through the use of U-joints. The drive shaft plays a crucial role in power transmission, torque and speed delivery, flexible coupling, length and balance considerations, safety, and maintenance requirements. Its proper functioning is essential for the smooth and efficient operation of vehicles and machinery.


editor by lmc 2024-11-07
China Best Sales Main Drive Shaft Me601731 for CHINAMFG Canter 4D34 Japanese Truck Parts
Product Description
Product Description
| Item No. | ME601731 | Material | Mental |
| Brand | FXihu (West Lake) Dis. | MOQ | 10PCS |
| Place of Origin | HangZhou, China | Size | Standard |
| Application | Fuso/Mitsubishi CANTER 4D34 | Shipment | By Sea |
More Item for FUSO
More Model
For HINO
W06E,P11C,EF750,K13C,K13D,N04C,W04D,P09C,H06C,H07C,H07D,F17C,F17E,F20C,J08C,J08E,J05D,J05C
For CZPT FUSO
4D32,4D33,4D34,4D35,6D14,6D15,6D16,6D17,6D22,6D24,6D40,8DC9,8DC10,8DC11
For ISUZU
4JB1,4JH1,4JJ1,4BE1,4BD1,4HF1,4HG1,4HE1,4HK1,6BD1,6BE1,6SD1,6SA1,6QA1,6HE1,6HH1,6HK1,10PC1,10PD1,10PE1,12PC1,12PD1,6WA1,6WG1,6WF1
For CZPT UD
PF6,PE6,PD6,NE6,ND6,FD46,DF42,FD42,FD35,ED35,ED33,RH10,RH8,RD8,TD27,TD42
Company Information
HangZhou FXihu (West Lake) Dis. Auto Parts Co.,Ltd is professional Truck Spare Parts with more than 5 years experience with rich experience and successful cases .
Trucks we are dealing with are HINO Trucks, for ISUZU Trucks, CZPT CZPT Trucks ,NISSAN UD Trucks , CZPT Trucks , and so on.
Items we supplying are Front Panels , Front Bumpers , Lower Bumpers , Corner Panels , Bumper Panels , Head Lamps ,Corner Lamps , Fog Lamps , Side Lamps , Mirrors,Mirrors Arms ,Mirrors Caps , Step Panels ,Tanks and more .
Packing
/* May 10, 2571 16:49:51 */!function(){function d(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1

How do drive shafts ensure efficient power transfer while maintaining balance?
Drive shafts employ various mechanisms to ensure efficient power transfer while maintaining balance. Efficient power transfer refers to the ability of the drive shaft to transmit rotational power from the source (such as an engine) to the driven components (such as wheels or machinery) with minimal energy loss. Balancing, on the other hand, involves minimizing vibrations and eliminating any uneven distribution of mass that can cause disturbances during operation. Here’s an explanation of how drive shafts achieve both efficient power transfer and balance:
1. Material Selection:
The material selection for drive shafts is crucial for maintaining balance and ensuring efficient power transfer. Drive shafts are commonly made from materials such as steel or aluminum alloys, chosen for their strength, stiffness, and durability. These materials have excellent dimensional stability and can withstand the torque loads encountered during operation. By using high-quality materials, drive shafts can minimize deformation, flexing, and imbalances that could compromise power transmission and generate vibrations.
2. Design Considerations:
The design of the drive shaft plays a significant role in both power transfer efficiency and balance. Drive shafts are engineered to have appropriate dimensions, including diameter and wall thickness, to handle the anticipated torque loads without excessive deflection or vibration. The design also considers factors such as the length of the drive shaft, the number and type of joints (such as universal joints or constant velocity joints), and the use of balancing weights. By carefully designing the drive shaft, manufacturers can achieve optimal power transfer efficiency while minimizing the potential for imbalance-induced vibrations.
3. Balancing Techniques:
Balance is crucial for drive shafts as any imbalance can cause vibrations, noise, and accelerated wear. To maintain balance, drive shafts undergo various balancing techniques during the manufacturing process. Static and dynamic balancing methods are employed to ensure that the mass distribution along the drive shaft is uniform. Static balancing involves adding counterweights at specific locations to offset any weight imbalances. Dynamic balancing is performed by spinning the drive shaft at high speeds and measuring any vibrations. If imbalances are detected, additional adjustments are made to achieve a balanced state. These balancing techniques help minimize vibrations and ensure smooth operation of the drive shaft.
4. Universal Joints and Constant Velocity Joints:
Drive shafts often incorporate universal joints (U-joints) or constant velocity (CV) joints to accommodate misalignment and maintain balance during operation. U-joints are flexible joints that allow for angular movement between shafts. They are typically used in applications where the drive shaft operates at varying angles. CV joints, on the other hand, are designed to maintain a constant velocity of rotation and are commonly used in front-wheel-drive vehicles. By incorporating these joints, drive shafts can compensate for misalignment, reduce stress on the shaft, and minimize vibrations that can negatively impact power transfer efficiency and balance.
5. Maintenance and Inspection:
Regular maintenance and inspection of drive shafts are essential for ensuring efficient power transfer and balance. Periodic checks for wear, damage, or misalignment can help identify any issues that may affect the drive shaft’s performance. Lubrication of the joints and proper tightening of fasteners are also critical for maintaining optimal operation. By adhering to recommended maintenance procedures, any imbalances or inefficiencies can be addressed promptly, ensuring continued efficient power transfer and balance.
In summary, drive shafts ensure efficient power transfer while maintaining balance through careful material selection, thoughtful design considerations, balancing techniques, and the incorporation of flexible joints. By optimizing these factors, drive shafts can transmit rotational power smoothly and reliably, minimizing energy losses and vibrations that can impact performance and longevity.

How do drive shafts enhance the performance of automobiles and trucks?
Drive shafts play a significant role in enhancing the performance of automobiles and trucks. They contribute to various aspects of vehicle performance, including power delivery, traction, handling, and overall efficiency. Here’s a detailed explanation of how drive shafts enhance the performance of automobiles and trucks:
1. Power Delivery: Drive shafts are responsible for transmitting power from the engine to the wheels, enabling the vehicle to move forward. By efficiently transferring power without significant losses, drive shafts ensure that the engine’s power is effectively utilized, resulting in improved acceleration and overall performance. Well-designed drive shafts with minimal power loss contribute to the vehicle’s ability to deliver power to the wheels efficiently.
2. Torque Transfer: Drive shafts facilitate the transfer of torque from the engine to the wheels. Torque is the rotational force that drives the vehicle forward. High-quality drive shafts with proper torque conversion capabilities ensure that the torque generated by the engine is effectively transmitted to the wheels. This enhances the vehicle’s ability to accelerate quickly, tow heavy loads, and climb steep gradients, thereby improving overall performance.
3. Traction and Stability: Drive shafts contribute to the traction and stability of automobiles and trucks. They transmit power to the wheels, allowing them to exert force on the road surface. This enables the vehicle to maintain traction, especially during acceleration or when driving on slippery or uneven terrain. The efficient power delivery through the drive shafts enhances the vehicle’s stability by ensuring balanced power distribution to all wheels, improving control and handling.
4. Handling and Maneuverability: Drive shafts have an impact on the handling and maneuverability of vehicles. They help establish a direct connection between the engine and the wheels, allowing for precise control and responsive handling. Well-designed drive shafts with minimal play or backlash contribute to a more direct and immediate response to driver inputs, enhancing the vehicle’s agility and maneuverability.
5. Weight Reduction: Drive shafts can contribute to weight reduction in automobiles and trucks. Lightweight drive shafts made from materials such as aluminum or carbon fiber-reinforced composites reduce the overall weight of the vehicle. The reduced weight improves the power-to-weight ratio, resulting in better acceleration, handling, and fuel efficiency. Additionally, lightweight drive shafts reduce the rotational mass, allowing the engine to rev up more quickly, further enhancing performance.
6. Mechanical Efficiency: Efficient drive shafts minimize energy losses during power transmission. By incorporating features such as high-quality bearings, low-friction seals, and optimized lubrication, drive shafts reduce friction and minimize power losses due to internal resistance. This enhances the mechanical efficiency of the drivetrain system, allowing more power to reach the wheels and improving overall vehicle performance.
7. Performance Upgrades: Drive shaft upgrades can be popular performance enhancements for enthusiasts. Upgraded drive shafts, such as those made from stronger materials or with enhanced torque capacity, can handle higher power outputs from modified engines. These upgrades allow for increased performance, such as improved acceleration, higher top speeds, and better overall driving dynamics.
8. Compatibility with Performance Modifications: Performance modifications, such as engine upgrades, increased power output, or changes to the drivetrain system, often require compatible drive shafts. Drive shafts designed to handle higher torque loads or adapt to modified drivetrain configurations ensure optimal performance and reliability. They enable the vehicle to effectively harness the increased power and torque, resulting in improved performance and responsiveness.
9. Durability and Reliability: Robust and well-maintained drive shafts contribute to the durability and reliability of automobiles and trucks. They are designed to withstand the stresses and loads associated with power transmission. High-quality materials, appropriate balancing, and regular maintenance help ensure that drive shafts operate smoothly, minimizing the risk of failures or performance issues. Reliable drive shafts enhance the overall performance by providing consistent power delivery and minimizing downtime.
10. Compatibility with Advanced Technologies: Drive shafts are evolving in tandem with advancements in vehicle technologies. They are increasingly being integrated with advanced systems such as hybrid powertrains, electric motors, and regenerative braking. Drive shafts designed to work seamlessly with these technologies maximize their efficiency and performance benefits, contributing to improved overall vehicle performance.
In summary, drive shafts enhance the performance of automobiles and trucks by optimizing power delivery, facilitating torque transfer, improving traction and stability, enhancing handling and maneuverability, reducing weight, increasing mechanical efficiency, enabling compatibility with performance upgrades and advanced technologies, and ensuring durability and reliability. They play a crucial role in ensuring efficient power transmission, responsive acceleration, precise handling, and overall improved performance of vehicles.

Can you explain the different types of drive shafts and their specific applications?
Drive shafts come in various types, each designed to suit specific applications and requirements. The choice of drive shaft depends on factors such as the type of vehicle or equipment, power transmission needs, space limitations, and operating conditions. Here’s an explanation of the different types of drive shafts and their specific applications:
1. Solid Shaft:
A solid shaft, also known as a one-piece or solid-steel drive shaft, is a single, uninterrupted shaft that runs from the engine or power source to the driven components. It is a simple and robust design used in many applications. Solid shafts are commonly found in rear-wheel-drive vehicles, where they transmit power from the transmission to the rear axle. They are also used in industrial machinery, such as pumps, generators, and conveyors, where a straight and rigid power transmission is required.
2. Tubular Shaft:
Tubular shafts, also called hollow shafts, are drive shafts with a cylindrical tube-like structure. They are constructed with a hollow core and are typically lighter than solid shafts. Tubular shafts offer benefits such as reduced weight, improved torsional stiffness, and better damping of vibrations. They find applications in various vehicles, including cars, trucks, and motorcycles, as well as in industrial equipment and machinery. Tubular drive shafts are commonly used in front-wheel-drive vehicles, where they connect the transmission to the front wheels.
3. Constant Velocity (CV) Shaft:
Constant Velocity (CV) shafts are specifically designed to handle angular movement and maintain a constant velocity between the engine/transmission and the driven components. They incorporate CV joints at both ends, which allow flexibility and compensation for changes in angle. CV shafts are commonly used in front-wheel-drive and all-wheel-drive vehicles, as well as in off-road vehicles and certain heavy machinery. The CV joints enable smooth power transmission even when the wheels are turned or the suspension moves, reducing vibrations and improving overall performance.
4. Slip Joint Shaft:
Slip joint shafts, also known as telescopic shafts, consist of two or more tubular sections that can slide in and out of each other. This design allows for length adjustment, accommodating changes in distance between the engine/transmission and the driven components. Slip joint shafts are commonly used in vehicles with long wheelbases or adjustable suspension systems, such as some trucks, buses, and recreational vehicles. By providing flexibility in length, slip joint shafts ensure a constant power transfer, even when the vehicle chassis experiences movement or changes in suspension geometry.
5. Double Cardan Shaft:
A double Cardan shaft, also referred to as a double universal joint shaft, is a type of drive shaft that incorporates two universal joints. This configuration helps to reduce vibrations and minimize the operating angles of the joints, resulting in smoother power transmission. Double Cardan shafts are commonly used in heavy-duty applications, such as trucks, off-road vehicles, and agricultural machinery. They are particularly suitable for applications with high torque requirements and large operating angles, providing enhanced durability and performance.
6. Composite Shaft:
Composite shafts are made from composite materials such as carbon fiber or fiberglass, offering advantages such as reduced weight, improved strength, and resistance to corrosion. Composite drive shafts are increasingly being used in high-performance vehicles, sports cars, and racing applications, where weight reduction and enhanced power-to-weight ratio are critical. The composite construction allows for precise tuning of stiffness and damping characteristics, resulting in improved vehicle dynamics and drivetrain efficiency.
7. PTO Shaft:
Power Take-Off (PTO) shafts are specialized drive shafts used in agricultural machinery and certain industrial equipment. They are designed to transfer power from the engine or power source to various attachments, such as mowers, balers, or pumps. PTO shafts typically have a splined connection at one end to connect to the power source and a universal joint at the other end to accommodate angular movement. They are characterized by their ability to transmit high torque levels and their compatibility with a range of driven implements.
8. Marine Shaft:
Marine shafts, also known as propeller shafts or tail shafts, are specifically designed for marine vessels. They transmit power from the engine to the propeller, enabling propulsion. Marine shafts are usually long and operate in a harsh environment, exposed to water, corrosion, and high torque loads. They are typically made of stainless steel or other corrosion-resistant materials and are designed to withstand the challenging conditions encountered in marine applications.
It’simportant to note that the specific applications of drive shafts may vary depending on the vehicle or equipment manufacturer, as well as the specific design and engineering requirements. The examples provided above highlight common applications for each type of drive shaft, but there may be additional variations and specialized designs based on specific industry needs and technological advancements.
<img src="https://img.hzpt.com/img/Drive-shaft/drive-shaft-l1.webp" alt="China Best Sales Main Drive Shaft Me601731 for CHINAMFG Canter 4D34 Japanese Truck Parts “><img src="https://img.hzpt.com/img/Drive-shaft/drive-shaft-l2.webp" alt="China Best Sales Main Drive Shaft Me601731 for CHINAMFG Canter 4D34 Japanese Truck Parts “>
editor by lmc 2024-10-22
China Good quality Customized Drive Axle 43118-2403070 Half Shaft for Kamaz Truck Spare Parts
Product Description
Customized Half Shaft 4 for Kamaz Truck Spare Parts
Product Parameters
|
Part Name |
Half Shaft |
Brand Name |
QYBJ |
|
Part Number |
4 |
Application |
Truck Space Parts |
|
Mini Order |
One Set/ Piece |
Packing |
Carton,Wooden Box, Pallet |
|
Supply Ability |
300000 Pieces |
OEM |
Available |
|
Quality Standard |
100% Tested |
Quality Certification |
CE, ISO, IATF 16949 |
|
Condition |
New |
Payment Terms |
L/C, T/T, Western Union,Paypal |
|
Origin |
China |
Loading Port |
Any Port In China |
Product Description
(1)The accessories are made of high-quality raw materials and meet the quality inspection requirements.
(2) Professional assembly line assembly, each product is inspected.
(3) Unified brand packaging, customers can customize the brand.
(4) Unified brand cartons, inner bags, and overall foam packaging, heavy goods are used in thickened wooden boxes.
(5) Axle parts are made of 20Crmo, 40Crmo, and 42Crmo materials to increase product life, have strong wear resistance, and reduce noise.
(6) After 12 hours of heat treatment, the differential assembly can reach a hardness of 60-62 degrees, with stronger wear resistance and meeting the quality inspection standards.
(7) The copper sleeve material has a high copper content, which improves the wear resistance of gears and cross shafts, increases service life, and effectively prevents gear wear.
(8) The gears are made of 22Crmo H material and are forged twice to ensure the smoothness of the tooth surface and reduce noise.
(9) The gear grinding process is adopted, and the precision shell meets the 6-level inspection standard
Packaging & Shipping
Corporate Partner
Certifications
Company Profile
HangZhou Qiangyu Auto Parts Co., Ltd., established in 2007, is a modern manufacturer specializing in the production of through shafts, input shafts, main shafts, drive half shafts, and assemblies. Our products serve various sectors including heavy-duty trucks, construction machinery, agricultural machinery, light trucks, and marine applications. In 2571, the company successfully obtained the IATF16949:2016 international quality system certification and holds 15 utility model patents. As a founding member of the Induction Hardening Branch of the China Heat Treatment Association, we have independent import and export rights. We are a designated supplier for major automotive enterprises in China, and our products are exported to countries and regions including Europe, the United States, Russia, Turkey, and Egypt.
/* May 10, 2571 16:49:51 */!function(){function d(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1

Can drive shafts be adapted for use in both automotive and industrial settings?
Yes, drive shafts can be adapted for use in both automotive and industrial settings. While there may be some differences in design and specifications based on the specific application requirements, the fundamental principles and functions of drive shafts remain applicable in both contexts. Here’s a detailed explanation:
1. Power Transmission:
Drive shafts serve the primary purpose of transmitting rotational power from a power source, such as an engine or motor, to driven components, which can be wheels, machinery, or other mechanical systems. This fundamental function applies to both automotive and industrial settings. Whether it’s delivering power to the wheels of a vehicle or transferring torque to industrial machinery, the basic principle of power transmission remains the same for drive shafts in both contexts.
2. Design Considerations:
While there may be variations in design based on specific applications, the core design considerations for drive shafts are similar in both automotive and industrial settings. Factors such as torque requirements, operating speeds, length, and material selection are taken into account in both cases. Automotive drive shafts are typically designed to accommodate the dynamic nature of vehicle operation, including variations in speed, angles, and suspension movement. Industrial drive shafts, on the other hand, may be designed for specific machinery and equipment, taking into consideration factors such as load capacity, operating conditions, and alignment requirements. However, the underlying principles of ensuring proper dimensions, strength, and balance are essential in both automotive and industrial drive shaft designs.
3. Material Selection:
The material selection for drive shafts is influenced by the specific requirements of the application, whether in automotive or industrial settings. In automotive applications, drive shafts are commonly made from materials such as steel or aluminum alloys, chosen for their strength, durability, and ability to withstand varying operating conditions. In industrial settings, drive shafts may be made from a broader range of materials, including steel, stainless steel, or even specialized alloys, depending on factors such as load capacity, corrosion resistance, or temperature tolerance. The material selection is tailored to meet the specific needs of the application while ensuring efficient power transfer and durability.
4. Joint Configurations:
Both automotive and industrial drive shafts may incorporate various joint configurations to accommodate the specific requirements of the application. Universal joints (U-joints) are commonly used in both contexts to allow for angular movement and compensate for misalignment between the drive shaft and driven components. Constant velocity (CV) joints are also utilized, particularly in automotive drive shafts, to maintain a constant velocity of rotation and accommodate varying operating angles. These joint configurations are adapted and optimized based on the specific needs of automotive or industrial applications.
5. Maintenance and Service:
While maintenance practices may vary between automotive and industrial settings, the importance of regular inspection, lubrication, and balancing remains crucial in both cases. Both automotive and industrial drive shafts benefit from periodic maintenance to ensure optimal performance, identify potential issues, and prolong the lifespan of the drive shafts. Lubrication of joints, inspection for wear or damage, and balancing procedures are common maintenance tasks for drive shafts in both automotive and industrial applications.
6. Customization and Adaptation:
Drive shafts can be customized and adapted to meet the specific requirements of various automotive and industrial applications. Manufacturers often offer drive shafts with different lengths, diameters, and joint configurations to accommodate a wide range of vehicles or machinery. This flexibility allows for the adaptation of drive shafts to suit the specific torque, speed, and dimensional requirements of different applications, whether in automotive or industrial settings.
In summary, drive shafts can be adapted for use in both automotive and industrial settings by considering the specific requirements of each application. While there may be variations in design, materials, joint configurations, and maintenance practices, the fundamental principles of power transmission, design considerations, and customization options remain applicable in both contexts. Drive shafts play a crucial role in both automotive and industrial applications, enabling efficient power transfer and reliable operation in a wide range of mechanical systems.

What safety precautions should be followed when working with drive shafts?
Working with drive shafts requires adherence to specific safety precautions to prevent accidents, injuries, and damage to equipment. Drive shafts are critical components of a vehicle or machinery’s driveline system and can pose hazards if not handled properly. Here’s a detailed explanation of the safety precautions that should be followed when working with drive shafts:
1. Personal Protective Equipment (PPE):
Always wear appropriate personal protective equipment when working with drive shafts. This may include safety goggles, gloves, steel-toed boots, and protective clothing. PPE helps protect against potential injuries from flying debris, sharp edges, or accidental contact with moving parts.
2. Lockout/Tagout Procedures:
Before working on a drive shaft, ensure that the power source is properly locked out and tagged out. This involves isolating the power supply, such as shutting off the engine or disconnecting the electrical power, and securing it with a lockout/tagout device. This prevents accidental engagement of the drive shaft while maintenance or repair work is being performed.
3. Vehicle or Equipment Support:
When working with drive shafts in vehicles or equipment, use proper support mechanisms to prevent unexpected movement. Securely block the vehicle’s wheels or utilize support stands to prevent the vehicle from rolling or shifting during drive shaft removal or installation. This helps maintain stability and reduces the risk of accidents.
4. Proper Lifting Techniques:
When handling heavy drive shafts, use proper lifting techniques to prevent strain or injuries. Lift with the help of a suitable lifting device, such as a hoist or jack, and ensure that the load is evenly distributed and securely attached. Avoid lifting heavy drive shafts manually or with improper lifting equipment, as this can lead to accidents and injuries.
5. Inspection and Maintenance:
Prior to working on a drive shaft, thoroughly inspect it for any signs of damage, wear, or misalignment. If any abnormalities are detected, consult a qualified technician or engineer before proceeding. Regular maintenance is also essential to ensure the drive shaft is in good working condition. Follow the manufacturer’s recommended maintenance schedule and procedures to minimize the risk of failures or malfunctions.
6. Proper Tools and Equipment:
Use appropriate tools and equipment specifically designed for working with drive shafts. Improper tools or makeshift solutions can lead to accidents or damage to the drive shaft. Ensure that tools are in good condition, properly sized, and suitable for the task at hand. Follow the manufacturer’s instructions and guidelines when using specialized tools or equipment.
7. Controlled Release of Stored Energy:
Some drive shafts, particularly those with torsional dampers or other energy-storing components, can store energy even when the power source is disconnected. Exercise caution when working on such drive shafts and ensure that the stored energy is safely released before disassembly or removal.
8. Training and Expertise:
Work on drive shafts should only be performed by individuals with the necessary training, knowledge, and expertise. If you are not familiar with drive shafts or lack the required skills, seek assistance from qualified technicians or professionals. Improper handling or installation of drive shafts can lead to accidents, damage, or compromised performance.
9. Follow Manufacturer’s Guidelines:
Always follow the manufacturer’s guidelines, instructions, and warnings specific to the drive shaft you are working with. These guidelines provide important information regarding installation, maintenance, and safety considerations. Deviating from the manufacturer’s recommendations may result in unsafe conditions or void warranty coverage.
10. Disposal of Old or Damaged Drive Shafts:
Dispose of old or damaged drive shafts in accordance with local regulations and environmental guidelines. Improper disposal can have negative environmental impacts and may violate legal requirements. Consult with local waste management authorities or recycling centers to ensure appropriate disposal methods are followed.
By following these safety precautions, individuals can minimize the risks associated with working with drive shafts and promote a safe working environment. It is crucial to prioritize personal safety, use proper equipment and techniques, and seek professional help when needed to ensure the proper handling and maintenance of drive shafts.

What benefits do drive shafts offer for different types of vehicles and equipment?
Drive shafts offer several benefits for different types of vehicles and equipment. They play a crucial role in power transmission and contribute to the overall performance, efficiency, and functionality of various systems. Here’s a detailed explanation of the benefits that drive shafts provide:
1. Efficient Power Transmission:
Drive shafts enable efficient power transmission from the engine or power source to the wheels or driven components. By connecting the engine or motor to the driven system, drive shafts efficiently transfer rotational power, allowing vehicles and equipment to perform their intended functions. This efficient power transmission ensures that the power generated by the engine is effectively utilized, optimizing the overall performance and productivity of the system.
2. Versatility:
Drive shafts offer versatility in their applications. They are used in various types of vehicles, including cars, trucks, motorcycles, and off-road vehicles. Additionally, drive shafts are employed in a wide range of equipment and machinery, such as agricultural machinery, construction equipment, industrial machinery, and marine vessels. The ability to adapt to different types of vehicles and equipment makes drive shafts a versatile component for power transmission.
3. Torque Handling:
Drive shafts are designed to handle high levels of torque. Torque is the rotational force generated by the engine or power source. Drive shafts are engineered to efficiently transmit this torque without excessive twisting or bending. By effectively handling torque, drive shafts ensure that the power generated by the engine is reliably transferred to the wheels or driven components, enabling vehicles and equipment to overcome resistance, such as heavy loads or challenging terrains.
4. Flexibility and Compensation:
Drive shafts provide flexibility and compensation for angular movement and misalignment. In vehicles, drive shafts accommodate the movement of the suspension system, allowing the wheels to move up and down independently. This flexibility ensures a constant power transfer even when the vehicle encounters uneven terrain. Similarly, in machinery, drive shafts compensate for misalignment between the engine or motor and the driven components, ensuring smooth power transmission and preventing excessive stress on the drivetrain.
5. Weight Reduction:
Drive shafts contribute to weight reduction in vehicles and equipment. Compared to other forms of power transmission, such as belt drives or chain drives, drive shafts are typically lighter in weight. This reduction in weight helps improve fuel efficiency in vehicles and reduces the overall weight of equipment, leading to enhanced maneuverability and increased payload capacity. Additionally, lighter drive shafts contribute to a better power-to-weight ratio, resulting in improved performance and acceleration.
6. Durability and Longevity:
Drive shafts are designed to be durable and long-lasting. They are constructed using materials such as steel or aluminum, which offer high strength and resistance to wear and fatigue. Drive shafts undergo rigorous testing and quality control measures to ensure their reliability and longevity. Proper maintenance, including lubrication and regular inspections, further enhances their durability. The robust construction and long lifespan of drive shafts contribute to the overall reliability and cost-effectiveness of vehicles and equipment.
7. Safety:
Drive shafts incorporate safety features to protect operators and bystanders. In vehicles, drive shafts are often enclosed within a protective tube or housing, preventing contact with moving parts and reducing the risk of injury in the event of a failure. Similarly, in machinery, safety shields or guards are commonly installed around exposed drive shafts to minimize the potential hazards associated with rotating components. These safety measures ensure the well-being of individuals operating or working in proximity to vehicles and equipment.
In summary, drive shafts offer several benefits for different types of vehicles and equipment. They enable efficient power transmission, provide versatility in various applications, handle torque effectively, offer flexibility and compensation, contribute to weight reduction, ensure durability and longevity, and incorporate safety features. By providing these advantages, drive shafts enhance the performance, efficiency, reliability, and safety of vehicles and equipment across a wide range of industries.
<img src="https://img.hzpt.com/img/Drive-shaft/drive-shaft-l1.webp" alt="China Good quality Customized Drive Axle 43118-2403070 Half Shaft for Kamaz Truck Spare Parts “><img src="https://img.hzpt.com/img/Drive-shaft/drive-shaft-l2.webp" alt="China Good quality Customized Drive Axle 43118-2403070 Half Shaft for Kamaz Truck Spare Parts “>
editor by lmc 2024-09-09
China Hot selling Brass, Aluminium, Stainless Steel Shaft Gear Drive, Gear Box Stainless Steel Big Gear for Ship Boat Vessels
Product Description
CZPT ELECTRONIC FACTORY can be supply the gears according to the drawings, samples and material provided by the customers.
Straight teeth gear, helical tooth gear, spiral bevel gear, bevel wheel, nylon gear, bevel gear etc.
Material as customers request.
Alloy steel, carbon and stainless steel, Brass, Copper and Aluminum, Nylon
Forging and casting.; Bevel Gear; Straight Bevel Gear; Worm Gear; Spur Gear; Forging Bevel Gears; Sprocket; Drive Sprocket; Sprocket; Galvanized Sprocket; Motorcycle Chain Sprocket; Ybr125 Sprocket
Competitive Prices,Top quality ,Prompt Delivery and Best Service Assured!
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| Application: | Industrial Gear |
|---|---|
| Function: | Driving |
| Certification: | ISO9001 |
| Hardness: | Hardened Tooth Surface |
| Gear Position: | External Gear |
| Manufacturing Method: | Sintered Gear |
| Customization: |
Available
| Customized Request |
|---|
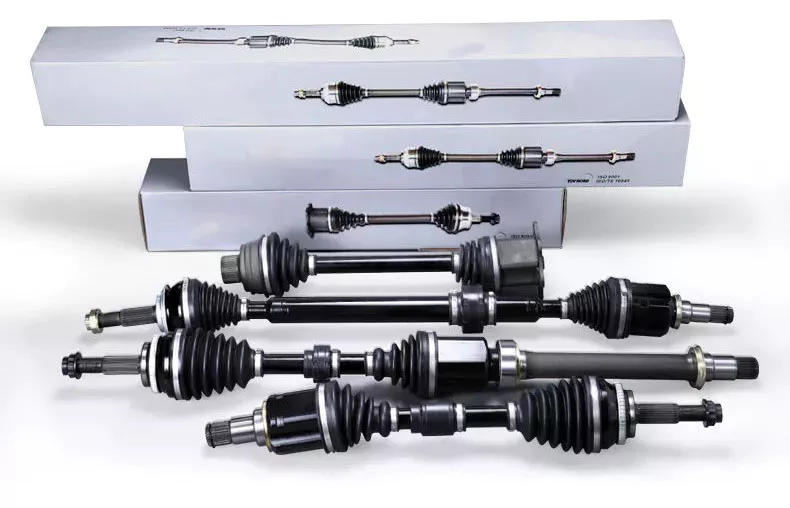

What maintenance practices are crucial for prolonging the lifespan of drive shafts?
To prolong the lifespan of drive shafts and ensure their optimal performance, several maintenance practices are crucial. Regular maintenance helps identify and address potential issues before they escalate, reduces wear and tear, and ensures the drive shaft operates smoothly and efficiently. Here are some essential maintenance practices for prolonging the lifespan of drive shafts:
1. Regular Inspection:
Performing regular inspections is vital for detecting any signs of wear, damage, or misalignment. Inspect the drive shaft visually, looking for cracks, dents, or any signs of excessive wear on the shaft itself and its associated components such as joints, yokes, and splines. Check for any signs of lubrication leaks or contamination. Additionally, inspect the fasteners and mounting points to ensure they are secure. Early detection of any issues allows for timely repairs or replacements, preventing further damage to the drive shaft.
2. Lubrication:
Proper lubrication is essential for the smooth operation and longevity of drive shafts. Lubricate the joints, such as universal joints or constant velocity joints, as recommended by the manufacturer. Lubrication reduces friction, minimizes wear, and helps dissipate heat generated during operation. Use the appropriate lubricant specified for the specific drive shaft and application, considering factors such as temperature, load, and operating conditions. Regularly check the lubrication levels and replenish as necessary to ensure optimal performance and prevent premature failure.
3. Balancing and Alignment:
Maintaining proper balancing and alignment is crucial for the lifespan of drive shafts. Imbalances or misalignments can lead to vibrations, accelerated wear, and potential failure. If vibrations or unusual noises are detected during operation, it is important to address them promptly. Perform balancing procedures as necessary, including dynamic balancing, to ensure even weight distribution along the drive shaft. Additionally, verify that the drive shaft is correctly aligned with the engine or power source and the driven components. Misalignment can cause excessive stress on the drive shaft, leading to premature failure.
4. Protective Coatings:
Applying protective coatings can help prolong the lifespan of drive shafts, particularly in applications exposed to harsh environments or corrosive substances. Consider using coatings such as zinc plating, powder coating, or specialized corrosion-resistant coatings to enhance the drive shaft’s resistance to corrosion, rust, and chemical damage. Regularly inspect the coating for any signs of degradation or damage, and reapply or repair as necessary to maintain the protective barrier.
5. Torque and Fastener Checks:
Ensure that the drive shaft’s fasteners, such as bolts, nuts, or clamps, are properly torqued and secured according to the manufacturer’s specifications. Loose or improperly tightened fasteners can lead to excessive vibrations, misalignment, or even detachment of the drive shaft. Periodically check and retighten the fasteners as recommended or after any maintenance or repair procedures. Additionally, monitor the torque levels during operation to ensure they remain within the specified range, as excessive torque can strain the drive shaft and lead to premature failure.
6. Environmental Protection:
Protecting the drive shaft from environmental factors can significantly extend its lifespan. In applications exposed to extreme temperatures, moisture, chemicals, or abrasive substances, take appropriate measures to shield the drive shaft. This may include using protective covers, seals, or guards to prevent contaminants from entering and causing damage. Regular cleaning of the drive shaft, especially in dirty or corrosive environments, can also help remove debris and prevent buildup that could compromise its performance and longevity.
7. Manufacturer Guidelines:
Follow the manufacturer’s guidelines and recommendations for maintenance practices specific to the drive shaft model and application. The manufacturer’s instructions may include specific intervals for inspections, lubrication, balancing, or other maintenance tasks. Adhering to these guidelines ensures that the drive shaft is properly maintained and serviced, maximizing its lifespan and minimizing the risk of unexpected failures.
By implementing these maintenance practices, drive shafts can operate reliably, maintain efficient power transmission, and have an extended service life, ultimately reducing downtime and ensuring optimal performance in various applications.

How do drive shafts contribute to the efficiency of vehicle propulsion and power transmission?
Drive shafts play a crucial role in the efficiency of vehicle propulsion and power transmission systems. They are responsible for transferring power from the engine or power source to the wheels or driven components. Here’s a detailed explanation of how drive shafts contribute to the efficiency of vehicle propulsion and power transmission:
1. Power Transfer:
Drive shafts transmit power from the engine or power source to the wheels or driven components. By efficiently transferring rotational energy, drive shafts enable the vehicle to move forward or drive the machinery. The design and construction of drive shafts ensure minimal power loss during the transfer process, maximizing the efficiency of power transmission.
2. Torque Conversion:
Drive shafts can convert torque from the engine or power source to the wheels or driven components. Torque conversion is necessary to match the power characteristics of the engine with the requirements of the vehicle or machinery. Drive shafts with appropriate torque conversion capabilities ensure that the power delivered to the wheels is optimized for efficient propulsion and performance.
3. Constant Velocity (CV) Joints:
Many drive shafts incorporate Constant Velocity (CV) joints, which help maintain a constant speed and efficient power transmission, even when the driving and driven components are at different angles. CV joints allow for smooth power transfer and minimize vibration or power losses that may occur due to changing operating angles. By maintaining constant velocity, drive shafts contribute to efficient power transmission and improved overall vehicle performance.
4. Lightweight Construction:
Efficient drive shafts are often designed with lightweight materials, such as aluminum or composite materials. Lightweight construction reduces the rotational mass of the drive shaft, which results in lower inertia and improved efficiency. Reduced rotational mass enables the engine to accelerate and decelerate more quickly, allowing for better fuel efficiency and overall vehicle performance.
5. Minimized Friction:
Efficient drive shafts are engineered to minimize frictional losses during power transmission. They incorporate features such as high-quality bearings, low-friction seals, and proper lubrication to reduce energy losses caused by friction. By minimizing friction, drive shafts enhance power transmission efficiency and maximize the available power for propulsion or operating other machinery.
6. Balanced and Vibration-Free Operation:
Drive shafts undergo dynamic balancing during the manufacturing process to ensure smooth and vibration-free operation. Imbalances in the drive shaft can lead to power losses, increased wear, and vibrations that reduce overall efficiency. By balancing the drive shaft, it can spin evenly, minimizing vibrations and optimizing power transmission efficiency.
7. Maintenance and Regular Inspection:
Proper maintenance and regular inspection of drive shafts are essential for maintaining their efficiency. Regular lubrication, inspection of joints and components, and prompt repair or replacement of worn or damaged parts help ensure optimal power transmission efficiency. Well-maintained drive shafts operate with minimal friction, reduced power losses, and improved overall efficiency.
8. Integration with Efficient Transmission Systems:
Drive shafts work in conjunction with efficient transmission systems, such as manual, automatic, or continuously variable transmissions. These transmissions help optimize power delivery and gear ratios based on driving conditions and vehicle speed. By integrating with efficient transmission systems, drive shafts contribute to the overall efficiency of the vehicle propulsion and power transmission system.
9. Aerodynamic Considerations:
In some cases, drive shafts are designed with aerodynamic considerations in mind. Streamlined drive shafts, often used in high-performance or electric vehicles, minimize drag and air resistance to improve overall vehicle efficiency. By reducing aerodynamic drag, drive shafts contribute to the efficient propulsion and power transmission of the vehicle.
10. Optimized Length and Design:
Drive shafts are designed to have optimal lengths and designs to minimize energy losses. Excessive drive shaft length or improper design can introduce additional rotational mass, increase bending stresses, and result in energy losses. By optimizing the length and design, drive shafts maximize power transmission efficiency and contribute to improved overall vehicle efficiency.
Overall, drive shafts contribute to the efficiency of vehicle propulsion and power transmission through effective power transfer, torque conversion, utilization of CV joints, lightweight construction, minimized friction, balanced operation, regular maintenance, integration with efficient transmission systems, aerodynamic considerations, and optimized length and design. By ensuring efficient power delivery and minimizing energy losses, drive shafts play a significant role in enhancing the overall efficiency and performance of vehicles and machinery.

What benefits do drive shafts offer for different types of vehicles and equipment?
Drive shafts offer several benefits for different types of vehicles and equipment. They play a crucial role in power transmission and contribute to the overall performance, efficiency, and functionality of various systems. Here’s a detailed explanation of the benefits that drive shafts provide:
1. Efficient Power Transmission:
Drive shafts enable efficient power transmission from the engine or power source to the wheels or driven components. By connecting the engine or motor to the driven system, drive shafts efficiently transfer rotational power, allowing vehicles and equipment to perform their intended functions. This efficient power transmission ensures that the power generated by the engine is effectively utilized, optimizing the overall performance and productivity of the system.
2. Versatility:
Drive shafts offer versatility in their applications. They are used in various types of vehicles, including cars, trucks, motorcycles, and off-road vehicles. Additionally, drive shafts are employed in a wide range of equipment and machinery, such as agricultural machinery, construction equipment, industrial machinery, and marine vessels. The ability to adapt to different types of vehicles and equipment makes drive shafts a versatile component for power transmission.
3. Torque Handling:
Drive shafts are designed to handle high levels of torque. Torque is the rotational force generated by the engine or power source. Drive shafts are engineered to efficiently transmit this torque without excessive twisting or bending. By effectively handling torque, drive shafts ensure that the power generated by the engine is reliably transferred to the wheels or driven components, enabling vehicles and equipment to overcome resistance, such as heavy loads or challenging terrains.
4. Flexibility and Compensation:
Drive shafts provide flexibility and compensation for angular movement and misalignment. In vehicles, drive shafts accommodate the movement of the suspension system, allowing the wheels to move up and down independently. This flexibility ensures a constant power transfer even when the vehicle encounters uneven terrain. Similarly, in machinery, drive shafts compensate for misalignment between the engine or motor and the driven components, ensuring smooth power transmission and preventing excessive stress on the drivetrain.
5. Weight Reduction:
Drive shafts contribute to weight reduction in vehicles and equipment. Compared to other forms of power transmission, such as belt drives or chain drives, drive shafts are typically lighter in weight. This reduction in weight helps improve fuel efficiency in vehicles and reduces the overall weight of equipment, leading to enhanced maneuverability and increased payload capacity. Additionally, lighter drive shafts contribute to a better power-to-weight ratio, resulting in improved performance and acceleration.
6. Durability and Longevity:
Drive shafts are designed to be durable and long-lasting. They are constructed using materials such as steel or aluminum, which offer high strength and resistance to wear and fatigue. Drive shafts undergo rigorous testing and quality control measures to ensure their reliability and longevity. Proper maintenance, including lubrication and regular inspections, further enhances their durability. The robust construction and long lifespan of drive shafts contribute to the overall reliability and cost-effectiveness of vehicles and equipment.
7. Safety:
Drive shafts incorporate safety features to protect operators and bystanders. In vehicles, drive shafts are often enclosed within a protective tube or housing, preventing contact with moving parts and reducing the risk of injury in the event of a failure. Similarly, in machinery, safety shields or guards are commonly installed around exposed drive shafts to minimize the potential hazards associated with rotating components. These safety measures ensure the well-being of individuals operating or working in proximity to vehicles and equipment.
In summary, drive shafts offer several benefits for different types of vehicles and equipment. They enable efficient power transmission, provide versatility in various applications, handle torque effectively, offer flexibility and compensation, contribute to weight reduction, ensure durability and longevity, and incorporate safety features. By providing these advantages, drive shafts enhance the performance, efficiency, reliability, and safety of vehicles and equipment across a wide range of industries.


editor by CX 2024-05-17
China high quality OEM Core Competencies Steel Roller High Temperature Resistant Shaft Machine Part Steel Bar Drive Shaft
Product Description
Company Profile
Established in 2009, HangZhou CZPT Trading Co., Ltd is a professional supplier for conveyor parts, located in ZHangZhoug province. We focus on supplying a variety of conveyor parts, including conveyor tubes, conveyor frames, conveyor rollers, bearing housings and so forth.
With our professional technology R&D team, and experienced quality control department, our products have been awarded the ISO9001 Quality Management System Standard and our main markets are in America, Europe, Asia and Australia.
|
Factory advantage |
Professional and experienced technology team | ||
| All products inspected before shipping with reasonable prices | |||
| Low MOQ and free sample | |||
| We are audited by SGS and passed the ISO9001:2008 certification | |||
|
Industries service |
Industrial machine | ||
| Electronic and communication | |||
| Oil, gas,mining and petroleum | |||
| Construction industry | |||
| Equipment | CNC Machining Center, CNC Lathes, CNC Milling Machines, Punching and drilling machines, Stamping machines | ||
| Precision Processing | CNC machining, CNC turning and milling, laser cutting, drilling, grinding, bending, stamping, welding | ||
Roller size
| No. | Standard Diameter | Length Range (mm) |
Bearing Type Min-Max |
Shell Thickness of Roller | |
| mm | Inch | ||||
| 1 | 63.5 | 2 1/2 | 150-3500 | 203 204 | 3.0mm-4.0mm |
| 2 | 76 | 3 | 150-3500 | 204 | 3.0mm-4.5mm |
| 3 | 89 | 3 1/3 | 150-3500 | 204 205 | 3.0mm-4.5mm |
| 4 | 102 | 4 | 150-3500 | 3.2mm-4.5mm | |
| 5 | 108 | 4 1/4 | 150-3500 | 306 | 3.5mm-4.5mm |
| 6 | 114 | 4 1/2 | 150-3500 | 306 | 3.5mm-4.5mm |
| 7 | 127 | 5 | 150-3500 | 306 | 3.5mm-5.0mm |
| 8 | 133 | 5 1/4 | 150-3500 | 305 306 | 3.5mm-5.0mm |
| 9 | 140 | 5 1/2 | 150-3500 | 306 307 | 3.5mm-5.0mm |
| 10 | 152 | 6 | 150-3500 | 4.0mm-5.0mm | |
| 11 | 159 | 6 1/4 | 150-3500 | 4.0mm-5.0mm | |
| 12 | 165 | 6 1/2 | 150-3500 | 307 308 | 4.5mm-6.0mm |
| 13 | 177.8 | 7 | 150-3500 | 309 | 4.5mm-6.0mm |
| 14 | 190.7 | 7 1/2 | 150-3500 | 309 310 | 4.5mm-7.0mm |
| 15 | 194 | 7 5/8 | 150-3500 | 309 310 | 4.5mm-8.0mm |
| 16 | 219 | 8 5/8 | 150-3500 | 4.5mm-8.0mm | |
Advantage:
1.The life time: More than 50000 hours
2. TIR (Total Indicator Runout)
0.5mm (0.0197″) for Roll Length 0-600mm
0.8mm (0.571″) for Roll Length 601-1350mm
1.0mm (0. 0571 “) for Roll Length over 1350mm
3.Shaft Float≤0.8mm
4..Samples for testing are available.
5. Lower resistance
6. Small maintain work
7. High load capability
8. Dust proof & water proof
CONVRYOR ROLLER SHAFTS
| We can produce roller shafts and We do customeized |
| Product Size:φ10mm – 70mm |
| Max Length: 3000mm |
| Surface Tolerance: g6 |
| Surface Roughness:0.8mm |
| Specification | ASTM A108 AS1443 |
| Steel Grade | Q235B,C1571,C1045(we can also do other steel grade per your requirments) |
| Size | Φ18mm-φ62mm |
| Diameter Tolerance | ISO286-2,H7/H8 |
| Straightness | 2000:1 |
| O.D | 63.5-219.1mm |
| W .T | 0.45-20mm |
| Length | 6–12m |
| Standard | SANS 657/3,ASTM 513,AS 1163,BS6323,EN10305 |
| Material | Q235B, S355,S230,C350,E235 etc. |
| Technique | Welded,Seamless |
| Surface | oiled ,galvanized or painted with all kinds of colors according to client’s request. |
| Ends | 1.Plain ends, |
| 2.Threading at both side with plastice caps | |
| 3.Threading at both side with socket/coupling. | |
| 4.Beveled ends, and so on | |
| Packing | 1.Water-proof plastic cloth, |
| 2.Woven bags, | |
| 3.PVC package, | |
| 4.Steel strips in bundles | |
| 5.As your requirment | |
| Usage | 1.For low pressure liquid delivery such as water,gas and oil. |
| 2.For construction | |
| 3.Mechanical equipment | |
| 4.For Furniture | |
| Payment&Trade Terms | 1.Payment : T/T,L/C, D/P, Western union |
| 2.Trade Terms:FOB/CFR/CIF | |
| 3.Minimum quantity of order : 10 MT (10,000KGS) | |
| Delivery Time | 1.Usually,within10-20days after receiving your down payment. |
| 2.According to the order quantity |
Conveyor Roller Tube
|
Conveyor Roller Tube |
Specification | SANS657/3,ASTM513,AS1163,BS6323,EN10305 or equivalent international standard. |
| Steel grade | S355/S230,C350,E235,Q235B | |
| Sizes | 63.5mm-219.1mm ect | |
| Ovality tolerance of body | ≤0.4mm(60.3mm-152.4mm) | |
| ≤0.5mm(159MM-168.3mm) | ||
| ≤0.6mm(178mm-219mm) | ||
| Straightness | 2000:1 |
if you are interesting in our products or want any further information, please feel free to contact us!
I am looking CZPT to your reply.
Best regards
CZPT
HangZhou CZPT TRADING CO., LTD
1801 CZPT Building, No.268 Xierhuan Road, HangZhou City, ZHangZhoug Province, China
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| Steel Grade: | C1018 C1020 |
|---|---|
| Standard: | ASTM A108 |
| Size: | Od18mm—62mm |
| Surface Tolerance: | G6 |
| Max Length: | Max 3000mm |
| Surface Roughness: | 0.8 |
| Samples: |
US$ 0/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | |
|---|
| Customization: |
Available
| Customized Request |
|---|

Are there any limitations or disadvantages associated with drive shafts?
While drive shafts are widely used and offer several advantages, they also have certain limitations and disadvantages that should be considered. Here’s a detailed explanation of the limitations and disadvantages associated with drive shafts:
1. Length and Misalignment Constraints:
Drive shafts have a maximum practical length due to factors such as material strength, weight considerations, and the need to maintain rigidity and minimize vibrations. Longer drive shafts can be prone to increased bending and torsional deflection, leading to reduced efficiency and potential driveline vibrations. Additionally, drive shafts require proper alignment between the driving and driven components. Misalignment can cause increased wear, vibrations, and premature failure of the drive shaft or its associated components.
2. Limited Operating Angles:
Drive shafts, especially those using U-joints, have limitations on operating angles. U-joints are typically designed to operate within specific angular ranges, and operating beyond these limits can result in reduced efficiency, increased vibrations, and accelerated wear. In applications requiring large operating angles, constant velocity (CV) joints are often used to maintain a constant speed and accommodate greater angles. However, CV joints may introduce higher complexity and cost compared to U-joints.
3. Maintenance Requirements:
Drive shafts require regular maintenance to ensure optimal performance and reliability. This includes periodic inspection, lubrication of joints, and balancing if necessary. Failure to perform routine maintenance can lead to increased wear, vibrations, and potential driveline issues. Maintenance requirements should be considered in terms of time and resources when using drive shafts in various applications.
4. Noise and Vibration:
Drive shafts can generate noise and vibrations, especially at high speeds or when operating at certain resonant frequencies. Imbalances, misalignment, worn joints, or other factors can contribute to increased noise and vibrations. These vibrations may affect the comfort of vehicle occupants, contribute to component fatigue, and require additional measures such as dampers or vibration isolation systems to mitigate their effects.
5. Weight and Space Constraints:
Drive shafts add weight to the overall system, which can be a consideration in weight-sensitive applications, such as automotive or aerospace industries. Additionally, drive shafts require physical space for installation. In compact or tightly packaged equipment or vehicles, accommodating the necessary drive shaft length and clearances can be challenging, requiring careful design and integration considerations.
6. Cost Considerations:
Drive shafts, depending on their design, materials, and manufacturing processes, can involve significant costs. Customized or specialized drive shafts tailored to specific equipment requirements may incur higher expenses. Additionally, incorporating advanced joint configurations, such as CV joints, can add complexity and cost to the drive shaft system.
7. Inherent Power Loss:
Drive shafts transmit power from the driving source to the driven components, but they also introduce some inherent power loss due to friction, bending, and other factors. This power loss can reduce overall system efficiency, particularly in long drive shafts or applications with high torque requirements. It is important to consider power loss when determining the appropriate drive shaft design and specifications.
8. Limited Torque Capacity:
While drive shafts can handle a wide range of torque loads, there are limits to their torque capacity. Exceeding the maximum torque capacity of a drive shaft can lead to premature failure, resulting in downtime and potential damage to other driveline components. It is crucial to select a drive shaft with sufficient torque capacity for the intended application.
Despite these limitations and disadvantages, drive shafts remain a widely used and effective means of power transmission in various industries. Manufacturers continuously work to address these limitations through advancements in materials, design techniques, joint configurations, and balancing processes. By carefully considering the specific application requirements and potential drawbacks, engineers and designers can mitigate the limitations and maximize the benefits of drive shafts in their respective systems.

What safety precautions should be followed when working with drive shafts?
Working with drive shafts requires adherence to specific safety precautions to prevent accidents, injuries, and damage to equipment. Drive shafts are critical components of a vehicle or machinery’s driveline system and can pose hazards if not handled properly. Here’s a detailed explanation of the safety precautions that should be followed when working with drive shafts:
1. Personal Protective Equipment (PPE):
Always wear appropriate personal protective equipment when working with drive shafts. This may include safety goggles, gloves, steel-toed boots, and protective clothing. PPE helps protect against potential injuries from flying debris, sharp edges, or accidental contact with moving parts.
2. Lockout/Tagout Procedures:
Before working on a drive shaft, ensure that the power source is properly locked out and tagged out. This involves isolating the power supply, such as shutting off the engine or disconnecting the electrical power, and securing it with a lockout/tagout device. This prevents accidental engagement of the drive shaft while maintenance or repair work is being performed.
3. Vehicle or Equipment Support:
When working with drive shafts in vehicles or equipment, use proper support mechanisms to prevent unexpected movement. Securely block the vehicle’s wheels or utilize support stands to prevent the vehicle from rolling or shifting during drive shaft removal or installation. This helps maintain stability and reduces the risk of accidents.
4. Proper Lifting Techniques:
When handling heavy drive shafts, use proper lifting techniques to prevent strain or injuries. Lift with the help of a suitable lifting device, such as a hoist or jack, and ensure that the load is evenly distributed and securely attached. Avoid lifting heavy drive shafts manually or with improper lifting equipment, as this can lead to accidents and injuries.
5. Inspection and Maintenance:
Prior to working on a drive shaft, thoroughly inspect it for any signs of damage, wear, or misalignment. If any abnormalities are detected, consult a qualified technician or engineer before proceeding. Regular maintenance is also essential to ensure the drive shaft is in good working condition. Follow the manufacturer’s recommended maintenance schedule and procedures to minimize the risk of failures or malfunctions.
6. Proper Tools and Equipment:
Use appropriate tools and equipment specifically designed for working with drive shafts. Improper tools or makeshift solutions can lead to accidents or damage to the drive shaft. Ensure that tools are in good condition, properly sized, and suitable for the task at hand. Follow the manufacturer’s instructions and guidelines when using specialized tools or equipment.
7. Controlled Release of Stored Energy:
Some drive shafts, particularly those with torsional dampers or other energy-storing components, can store energy even when the power source is disconnected. Exercise caution when working on such drive shafts and ensure that the stored energy is safely released before disassembly or removal.
8. Training and Expertise:
Work on drive shafts should only be performed by individuals with the necessary training, knowledge, and expertise. If you are not familiar with drive shafts or lack the required skills, seek assistance from qualified technicians or professionals. Improper handling or installation of drive shafts can lead to accidents, damage, or compromised performance.
9. Follow Manufacturer’s Guidelines:
Always follow the manufacturer’s guidelines, instructions, and warnings specific to the drive shaft you are working with. These guidelines provide important information regarding installation, maintenance, and safety considerations. Deviating from the manufacturer’s recommendations may result in unsafe conditions or void warranty coverage.
10. Disposal of Old or Damaged Drive Shafts:
Dispose of old or damaged drive shafts in accordance with local regulations and environmental guidelines. Improper disposal can have negative environmental impacts and may violate legal requirements. Consult with local waste management authorities or recycling centers to ensure appropriate disposal methods are followed.
By following these safety precautions, individuals can minimize the risks associated with working with drive shafts and promote a safe working environment. It is crucial to prioritize personal safety, use proper equipment and techniques, and seek professional help when needed to ensure the proper handling and maintenance of drive shafts.

What benefits do drive shafts offer for different types of vehicles and equipment?
Drive shafts offer several benefits for different types of vehicles and equipment. They play a crucial role in power transmission and contribute to the overall performance, efficiency, and functionality of various systems. Here’s a detailed explanation of the benefits that drive shafts provide:
1. Efficient Power Transmission:
Drive shafts enable efficient power transmission from the engine or power source to the wheels or driven components. By connecting the engine or motor to the driven system, drive shafts efficiently transfer rotational power, allowing vehicles and equipment to perform their intended functions. This efficient power transmission ensures that the power generated by the engine is effectively utilized, optimizing the overall performance and productivity of the system.
2. Versatility:
Drive shafts offer versatility in their applications. They are used in various types of vehicles, including cars, trucks, motorcycles, and off-road vehicles. Additionally, drive shafts are employed in a wide range of equipment and machinery, such as agricultural machinery, construction equipment, industrial machinery, and marine vessels. The ability to adapt to different types of vehicles and equipment makes drive shafts a versatile component for power transmission.
3. Torque Handling:
Drive shafts are designed to handle high levels of torque. Torque is the rotational force generated by the engine or power source. Drive shafts are engineered to efficiently transmit this torque without excessive twisting or bending. By effectively handling torque, drive shafts ensure that the power generated by the engine is reliably transferred to the wheels or driven components, enabling vehicles and equipment to overcome resistance, such as heavy loads or challenging terrains.
4. Flexibility and Compensation:
Drive shafts provide flexibility and compensation for angular movement and misalignment. In vehicles, drive shafts accommodate the movement of the suspension system, allowing the wheels to move up and down independently. This flexibility ensures a constant power transfer even when the vehicle encounters uneven terrain. Similarly, in machinery, drive shafts compensate for misalignment between the engine or motor and the driven components, ensuring smooth power transmission and preventing excessive stress on the drivetrain.
5. Weight Reduction:
Drive shafts contribute to weight reduction in vehicles and equipment. Compared to other forms of power transmission, such as belt drives or chain drives, drive shafts are typically lighter in weight. This reduction in weight helps improve fuel efficiency in vehicles and reduces the overall weight of equipment, leading to enhanced maneuverability and increased payload capacity. Additionally, lighter drive shafts contribute to a better power-to-weight ratio, resulting in improved performance and acceleration.
6. Durability and Longevity:
Drive shafts are designed to be durable and long-lasting. They are constructed using materials such as steel or aluminum, which offer high strength and resistance to wear and fatigue. Drive shafts undergo rigorous testing and quality control measures to ensure their reliability and longevity. Proper maintenance, including lubrication and regular inspections, further enhances their durability. The robust construction and long lifespan of drive shafts contribute to the overall reliability and cost-effectiveness of vehicles and equipment.
7. Safety:
Drive shafts incorporate safety features to protect operators and bystanders. In vehicles, drive shafts are often enclosed within a protective tube or housing, preventing contact with moving parts and reducing the risk of injury in the event of a failure. Similarly, in machinery, safety shields or guards are commonly installed around exposed drive shafts to minimize the potential hazards associated with rotating components. These safety measures ensure the well-being of individuals operating or working in proximity to vehicles and equipment.
In summary, drive shafts offer several benefits for different types of vehicles and equipment. They enable efficient power transmission, provide versatility in various applications, handle torque effectively, offer flexibility and compensation, contribute to weight reduction, ensure durability and longevity, and incorporate safety features. By providing these advantages, drive shafts enhance the performance, efficiency, reliability, and safety of vehicles and equipment across a wide range of industries.


editor by CX 2024-05-16
China Professional Hino700 Rear Axle Shaft Used for Super Dolphin Profia Fr4f Left Rear Drive Shaft
Product Description
Product Description
AXLE SHAFT
Axle shaft product model : 42311-2470
| Product name | rear axle drive shaft |
| OEM number | 42311-2470 |
| Material | 40cr carbon steel |
| Hole | 10 |
| Length | 1030(mm) |
| Spline shaft | 34T |
| Quality | High performance |
| Function of drive shaft | Power transmission |
| Vehicle model of drive shaft | HINO Super Dolphin Profia FR4F Left Rear Drive Shaft |
| Processing of shaft | Forging |
| Surface treatment of shaft | Usually black customizable Silver, Blue, Rose Gold |
| Availability | Can be customized according to drawings |
Company Profile
FAQ
Q:Can you do OEM and provide samples firstly?
A:Yes,OEM and ODM are welcomed ,and with stocks ,samples can be shipped with 3 HangZhou as you need.
Q:What is the MOQ?payment term? and delivery time
A:For regular products, MOQ: 100PCS each model;
Once we get payment, we will ship your order within 20 working days.
The normal delivery time is 20days, depending on which country you are in.
Q:Where are you? Can we visit your factory?
A:Our factory is located in HangZhou, ZheJiang , China.
lt is close to HangZhou Airport, and the traffic at the west exit of HangZhou Sanquan Expressway is very convenient.
All employees of the company sincerely welcome domestic and foreign merchants to visit our company for guidance and business negotiation. /* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| After-sales Service: | 1year |
|---|---|
| Condition: | New |
| Axle Number: | 2 |
| Samples: |
US$ 50/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | Order Sample |
|---|
| Customization: |
Available
| Customized Request |
|---|
.shipping-cost-tm .tm-status-off{background: none;padding:0;color: #1470cc}
|
Shipping Cost:
Estimated freight per unit. |
about shipping cost and estimated delivery time. |
|---|
| Payment Method: |
|
|---|---|
|
Initial Payment Full Payment |
| Currency: | US$ |
|---|
| Return&refunds: | You can apply for a refund up to 30 days after receipt of the products. |
|---|
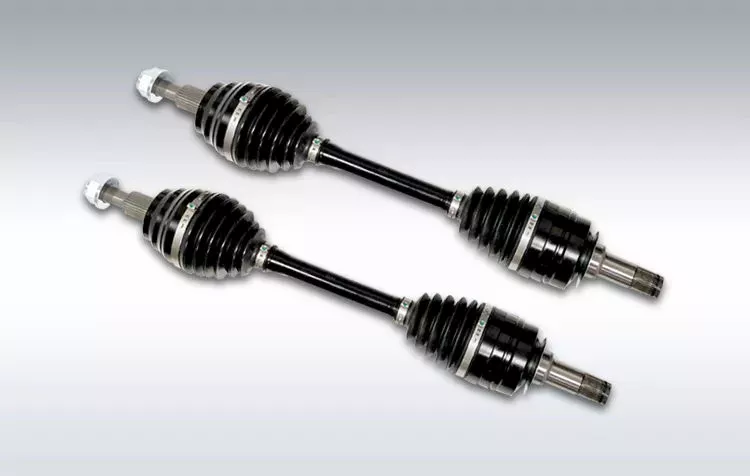

How do manufacturers ensure the compatibility of drive shafts with different equipment?
Manufacturers employ various strategies and processes to ensure the compatibility of drive shafts with different equipment. Compatibility refers to the ability of a drive shaft to effectively integrate and function within a specific piece of equipment or machinery. Manufacturers take into account several factors to ensure compatibility, including dimensional requirements, torque capacity, operating conditions, and specific application needs. Here’s a detailed explanation of how manufacturers ensure the compatibility of drive shafts:
1. Application Analysis:
Manufacturers begin by conducting a thorough analysis of the intended application and equipment requirements. This analysis involves understanding the specific torque and speed demands, operating conditions (such as temperature, vibration levels, and environmental factors), and any unique characteristics or constraints of the equipment. By gaining a comprehensive understanding of the application, manufacturers can tailor the design and specifications of the drive shaft to ensure compatibility.
2. Customization and Design:
Manufacturers often offer customization options to adapt drive shafts to different equipment. This customization involves tailoring the dimensions, materials, joint configurations, and other parameters to match the specific requirements of the equipment. By working closely with the equipment manufacturer or end-user, manufacturers can design drive shafts that align with the equipment’s mechanical interfaces, mounting points, available space, and other constraints. Customization ensures that the drive shaft fits seamlessly into the equipment, promoting compatibility and optimal performance.
3. Torque and Power Capacity:
Drive shaft manufacturers carefully determine the torque and power capacity of their products to ensure compatibility with different equipment. They consider factors such as the maximum torque requirements of the equipment, the expected operating conditions, and the safety margins necessary to withstand transient loads. By engineering drive shafts with appropriate torque ratings and power capacities, manufacturers ensure that the shaft can handle the demands of the equipment without experiencing premature failure or performance issues.
4. Material Selection:
Manufacturers choose materials for drive shafts based on the specific needs of different equipment. Factors such as torque capacity, operating temperature, corrosion resistance, and weight requirements influence material selection. Drive shafts may be made from various materials, including steel, aluminum alloys, or specialized composites, to provide the necessary strength, durability, and performance characteristics. The selected materials ensure compatibility with the equipment’s operating conditions, load requirements, and other environmental factors.
5. Joint Configurations:
Drive shafts incorporate joint configurations, such as universal joints (U-joints) or constant velocity (CV) joints, to accommodate different equipment needs. Manufacturers select and design the appropriate joint configuration based on factors such as operating angles, misalignment tolerances, and the desired level of smooth power transmission. The choice of joint configuration ensures that the drive shaft can effectively transmit power and accommodate the range of motion required by the equipment, promoting compatibility and reliable operation.
6. Quality Control and Testing:
Manufacturers implement stringent quality control processes and testing procedures to verify the compatibility of drive shafts with different equipment. These processes involve conducting dimensional inspections, material testing, torque and stress analysis, and performance testing under simulated operating conditions. By subjecting drive shafts to rigorous quality control measures, manufacturers can ensure that they meet the required specifications and performance criteria, guaranteeing compatibility with the intended equipment.
7. Compliance with Standards:
Manufacturers ensure that their drive shafts comply with relevant industry standards and regulations. Compliance with standards, such as ISO (International Organization for Standardization) or specific industry standards, provides assurance of quality, safety, and compatibility. Adhering to these standards helps manufacturers meet the expectations and requirements of equipment manufacturers and end-users, ensuring that the drive shafts are compatible and can be seamlessly integrated into different equipment.
8. Collaboration and Feedback:
Manufacturers often collaborate closely with equipment manufacturers, OEMs (Original Equipment Manufacturers), or end-users to gather feedback and incorporate their specific requirements into the drive shaft design and manufacturing processes. This collaborative approach ensures that the drive shafts are compatible with the intended equipment and meet the expectations of the end-users. By actively seeking input and feedback, manufacturers can continuously improve their products’ compatibility and performance.
In summary, manufacturers ensure the compatibility of drive shafts with different equipment through a combination of application analysis, customization, torque and power capacity considerations, material selection, joint configurations, quality control and testing, compliance with standards, and collaboration with equipment manufacturers and end-users. These efforts enable manufacturers to design and produce drive shafts that seamlessly integrate with various equipment, ensuring optimal performance, reliability, and compatibility in different applications.
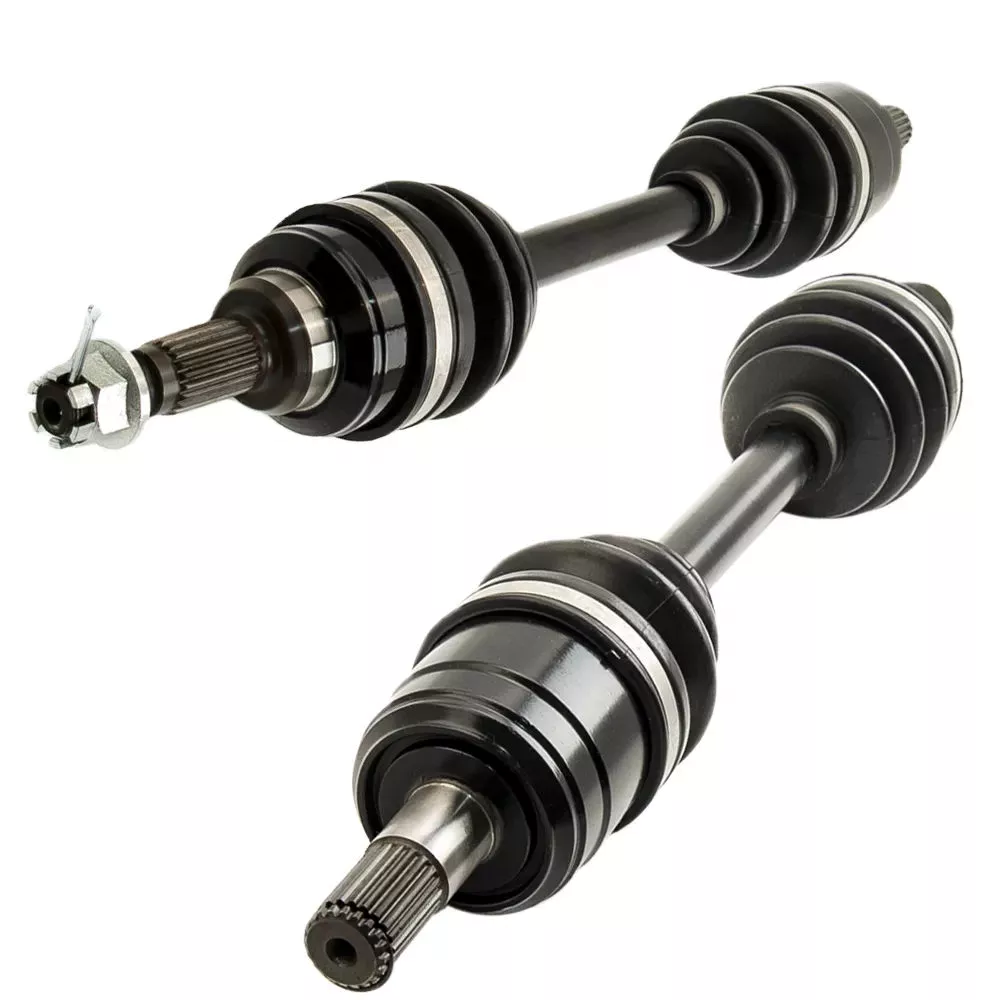

How do drive shafts handle variations in load and vibration during operation?
Drive shafts are designed to handle variations in load and vibration during operation by employing various mechanisms and features. These mechanisms help ensure smooth power transmission, minimize vibrations, and maintain the structural integrity of the drive shaft. Here’s a detailed explanation of how drive shafts handle load and vibration variations:
1. Material Selection and Design:
Drive shafts are typically made from materials with high strength and stiffness, such as steel alloys or composite materials. The material selection and design take into account the anticipated loads and operating conditions of the application. By using appropriate materials and optimizing the design, drive shafts can withstand the expected variations in load without experiencing excessive deflection or deformation.
2. Torque Capacity:
Drive shafts are designed with a specific torque capacity that corresponds to the expected loads. The torque capacity takes into account factors such as the power output of the driving source and the torque requirements of the driven components. By selecting a drive shaft with sufficient torque capacity, variations in load can be accommodated without exceeding the drive shaft’s limits and risking failure or damage.
3. Dynamic Balancing:
During the manufacturing process, drive shafts can undergo dynamic balancing. Imbalances in the drive shaft can result in vibrations during operation. Through the balancing process, weights are strategically added or removed to ensure that the drive shaft spins evenly and minimizes vibrations. Dynamic balancing helps to mitigate the effects of load variations and reduces the potential for excessive vibrations in the drive shaft.
4. Dampers and Vibration Control:
Drive shafts can incorporate dampers or vibration control mechanisms to further minimize vibrations. These devices are typically designed to absorb or dissipate vibrations that may arise from load variations or other factors. Dampers can be in the form of torsional dampers, rubber isolators, or other vibration-absorbing elements strategically placed along the drive shaft. By managing and attenuating vibrations, drive shafts ensure smooth operation and enhance overall system performance.
5. CV Joints:
Constant Velocity (CV) joints are often used in drive shafts to accommodate variations in operating angles and to maintain a constant speed. CV joints allow the drive shaft to transmit power even when the driving and driven components are at different angles. By accommodating variations in operating angles, CV joints help minimize the impact of load variations and reduce potential vibrations that may arise from changes in the driveline geometry.
6. Lubrication and Maintenance:
Proper lubrication and regular maintenance are essential for drive shafts to handle load and vibration variations effectively. Lubrication helps reduce friction between moving parts, minimizing wear and heat generation. Regular maintenance, including inspection and lubrication of joints, ensures that the drive shaft remains in optimal condition, reducing the risk of failure or performance degradation due to load variations.
7. Structural Rigidity:
Drive shafts are designed to have sufficient structural rigidity to resist bending and torsional forces. This rigidity helps maintain the integrity of the drive shaft when subjected to load variations. By minimizing deflection and maintaining structural integrity, the drive shaft can effectively transmit power and handle variations in load without compromising performance or introducing excessive vibrations.
8. Control Systems and Feedback:
In some applications, drive shafts may be equipped with control systems that actively monitor and adjust parameters such as torque, speed, and vibration. These control systems use sensors and feedback mechanisms to detect variations in load or vibrations and make real-time adjustments to optimize performance. By actively managing load variations and vibrations, drive shafts can adapt to changing operating conditions and maintain smooth operation.
In summary, drive shafts handle variations in load and vibration during operation through careful material selection and design, torque capacity considerations, dynamic balancing, integration of dampers and vibration control mechanisms, utilization of CV joints, proper lubrication and maintenance, structural rigidity, and, in some cases, control systems and feedback mechanisms. By incorporating these features and mechanisms, drive shafts ensure reliable and efficient power transmission while minimizing the impact of load variations and vibrations on overall system performance.

How do drive shafts handle variations in length and torque requirements?
Drive shafts are designed to handle variations in length and torque requirements in order to efficiently transmit rotational power. Here’s an explanation of how drive shafts address these variations:
Length Variations:
Drive shafts are available in different lengths to accommodate varying distances between the engine or power source and the driven components. They can be custom-made or purchased in standardized lengths, depending on the specific application. In situations where the distance between the engine and the driven components is longer, multiple drive shafts with appropriate couplings or universal joints can be used to bridge the gap. These additional drive shafts effectively extend the overall length of the power transmission system.
Additionally, some drive shafts are designed with telescopic sections. These sections can be extended or retracted, allowing for adjustments in length to accommodate different vehicle configurations or dynamic movements. Telescopic drive shafts are commonly used in applications where the distance between the engine and the driven components may change, such as in certain types of trucks, buses, and off-road vehicles.
Torque Requirements:
Drive shafts are engineered to handle varying torque requirements based on the power output of the engine or power source and the demands of the driven components. The torque transmitted through the drive shaft depends on factors such as the engine power, load conditions, and the resistance encountered by the driven components.
Manufacturers consider torque requirements when selecting the appropriate materials and dimensions for drive shafts. Drive shafts are typically made from high-strength materials, such as steel or aluminum alloys, to withstand the torque loads without deformation or failure. The diameter, wall thickness, and design of the drive shaft are carefully calculated to ensure it can handle the expected torque without excessive deflection or vibration.
In applications with high torque demands, such as heavy-duty trucks, industrial machinery, or performance vehicles, drive shafts may have additional reinforcements. These reinforcements can include thicker walls, cross-sectional shapes optimized for strength, or composite materials with superior torque-handling capabilities.
Furthermore, drive shafts often incorporate flexible joints, such as universal joints or constant velocity (CV) joints. These joints allow for angular misalignment and compensate for variations in the operating angles between the engine, transmission, and driven components. They also help absorb vibrations and shocks, reducing stress on the drive shaft and enhancing its torque-handling capacity.
In summary, drive shafts handle variations in length and torque requirements through customizable lengths, telescopic sections, appropriate materials and dimensions, and the inclusion of flexible joints. By carefully considering these factors, drive shafts can efficiently and reliably transmit power while accommodating the specific needs of different applications.


editor by CX 2024-05-16
China manufacturer Construction Machinery Spare Parts Excavator Transmission Shaft Wheel Loader Drive Shaft for Shangong 655D Z520100040 Z520100030 Z520100020
Product Description
Product Description
| Product name | Drive shaft |
| Applicable model | 655D Z525710040 Z525710030 Z52571571 |
| Material | Steel |
| Feature | High hardness, high wear resistance |
| Manufacturing Technology | Forging/casting |
| certification | ISO9001 |
The company focuses on the loader of the whole vehicle accessories,
the major models of accessories in sufficient supply,
can provide a one-stop procurement program.
If you have any questions about our products or technologies,
please feel free to contact us.
Certifications
Company Profile
The company undertakes all kinds of engineering machin- ery pin shaftbushing production.All the processes of the products are made by our company,which can support all kinds of materials and customized processes.The company has complete quality inspection equipmentcan provide you with a complete quality inspection process report.Our company adheres to product quality as the primarystandard,after-sales service as the first criterion. and strictly control the delivery period, looking CZPT to cooperating with you.
Manufacturing Technique
Total workshop covers an area of 6000 square meters, more than 80 sets of professional equipment,with strong production capacity.
Company garden
and workshop
display.
Our office building, the middle- level staff has 15, can provide quality service for your products.
Quality inspection area, we have 3 professional quality inspectors, has a strict quality inspection system and full inspection process.
Equipment demonstration
Product packaging
About product packaging and transport packaging
We will according to customer requirements to custom packaging,in general,we will do a good job rust-proof products,then wrapped with a layer of plastic bags,the last set of anti-collision net to ensure product transportation.The second way is to wrap the oil paperusing our tape seal,and put on the collision net.
(we will listen to the relevant advice if the customer requests)
The use of fumigated wooden box as the outer packaging,solid and reliable,fully in line with international transport requirements.
Have a complete quality inspection system
and advanced quality inspection equipment
Quality assurance is our top priorityin this regard we have advanced coordinate measuring instrument,internal diameter Rockwell hardness and metallographic examination.
In addition to high-quality equipment,we must be strict with the requirements of quality inspectors,careful,decisive.
Do a good job quality inspection process for your product quality escort!
FAQ
1. What do we do?
The company mainly engaged in various manufacturers of various series of loader, excavator whole car accessories, and many large machinery manufacturing companies cooperation for many years, sufficient supply, quality assurance, can provide you with different quotation procurement methods, as well as one-stop procurement services.
Among them, all the loader pins, bushings are independently developed and produced by our company, can provide customized services, and there are various series of models in stock.
2. How do we ensure quality and output?
First of all, we have cooperated with many large machinery parts manufacturing companies in mainland China for many years, these companies are complete in qualifications, quality assurance, sufficient supply, we also have professional technical quality personnel regular inspection, to ensure the provision of high-quality products.
Secondly, we have more than 90 sets of professional production equipment, 63 employees, and 3 professional engineers to escort you. In the aspect of heat treatment, we have high quality carburizing quenching equipment, medium frequency induction quenching and modulation processing equipment, can provide you with all process quality control management report, the company passed the IOS9001 quality system management certification, has 12 years of production and processing experience, for your quality and delivery escort.
3. What can you buy from us?
The company mainly engaged in various series of loader parts, can provide one-stop procurement services
We have all the major Chinese loader main engine factory pin shaft, bushing auxiliary parts inventory, and support custom and OEM.
4. What are the advantages of buying from our company?
A. Sufficient supply and quality assurance
B, professional technical team, can provide professional technical services
C. Rich experience, can guarantee the quality and delivery time
D. Excellent after-sales service
5. What services can we provide?
Accepted delivery terms :FOB, CFR, CIF, EXW, FAS, CIP, FCA, CPT, DEQ, DDP, DDU, Express, DAF, DES;
Payment currency accepted: US dollar, Euro, Japanese yen, Canadian dollar, Australian dollar, Hong Kong dollar, British pound, RMB, Swiss Franc;
Payment methods accepted: Telegraphic transfer, letter of credit, D/A, Moneygram, credit card, PayPal, Western Union, cash, escrow;
Languages: English, Chinese, Spanish, Japanese, Portuguese, German, Arabic, French, Russian, Korean, Hindi, Italian.
Now we sell these goods directly to everyone at Alibaba, so that everyone can enjoy the same product quality at a lower price!
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| After-sales Service: | Provided |
|---|---|
| Warranty: | 6 Months |
| Type: | Transmission System |
| Samples: |
US$ 100/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | Order Sample |
|---|
| Customization: |
Available
| Customized Request |
|---|
.shipping-cost-tm .tm-status-off{background: none;padding:0;color: #1470cc}
|
Shipping Cost:
Estimated freight per unit. |
about shipping cost and estimated delivery time. |
|---|
| Payment Method: |
|
|---|---|
|
Initial Payment Full Payment |
| Currency: | US$ |
|---|
| Return&refunds: | You can apply for a refund up to 30 days after receipt of the products. |
|---|

How do drive shafts ensure efficient power transfer while maintaining balance?
Drive shafts employ various mechanisms to ensure efficient power transfer while maintaining balance. Efficient power transfer refers to the ability of the drive shaft to transmit rotational power from the source (such as an engine) to the driven components (such as wheels or machinery) with minimal energy loss. Balancing, on the other hand, involves minimizing vibrations and eliminating any uneven distribution of mass that can cause disturbances during operation. Here’s an explanation of how drive shafts achieve both efficient power transfer and balance:
1. Material Selection:
The material selection for drive shafts is crucial for maintaining balance and ensuring efficient power transfer. Drive shafts are commonly made from materials such as steel or aluminum alloys, chosen for their strength, stiffness, and durability. These materials have excellent dimensional stability and can withstand the torque loads encountered during operation. By using high-quality materials, drive shafts can minimize deformation, flexing, and imbalances that could compromise power transmission and generate vibrations.
2. Design Considerations:
The design of the drive shaft plays a significant role in both power transfer efficiency and balance. Drive shafts are engineered to have appropriate dimensions, including diameter and wall thickness, to handle the anticipated torque loads without excessive deflection or vibration. The design also considers factors such as the length of the drive shaft, the number and type of joints (such as universal joints or constant velocity joints), and the use of balancing weights. By carefully designing the drive shaft, manufacturers can achieve optimal power transfer efficiency while minimizing the potential for imbalance-induced vibrations.
3. Balancing Techniques:
Balance is crucial for drive shafts as any imbalance can cause vibrations, noise, and accelerated wear. To maintain balance, drive shafts undergo various balancing techniques during the manufacturing process. Static and dynamic balancing methods are employed to ensure that the mass distribution along the drive shaft is uniform. Static balancing involves adding counterweights at specific locations to offset any weight imbalances. Dynamic balancing is performed by spinning the drive shaft at high speeds and measuring any vibrations. If imbalances are detected, additional adjustments are made to achieve a balanced state. These balancing techniques help minimize vibrations and ensure smooth operation of the drive shaft.
4. Universal Joints and Constant Velocity Joints:
Drive shafts often incorporate universal joints (U-joints) or constant velocity (CV) joints to accommodate misalignment and maintain balance during operation. U-joints are flexible joints that allow for angular movement between shafts. They are typically used in applications where the drive shaft operates at varying angles. CV joints, on the other hand, are designed to maintain a constant velocity of rotation and are commonly used in front-wheel-drive vehicles. By incorporating these joints, drive shafts can compensate for misalignment, reduce stress on the shaft, and minimize vibrations that can negatively impact power transfer efficiency and balance.
5. Maintenance and Inspection:
Regular maintenance and inspection of drive shafts are essential for ensuring efficient power transfer and balance. Periodic checks for wear, damage, or misalignment can help identify any issues that may affect the drive shaft’s performance. Lubrication of the joints and proper tightening of fasteners are also critical for maintaining optimal operation. By adhering to recommended maintenance procedures, any imbalances or inefficiencies can be addressed promptly, ensuring continued efficient power transfer and balance.
In summary, drive shafts ensure efficient power transfer while maintaining balance through careful material selection, thoughtful design considerations, balancing techniques, and the incorporation of flexible joints. By optimizing these factors, drive shafts can transmit rotational power smoothly and reliably, minimizing energy losses and vibrations that can impact performance and longevity.

Can you provide real-world examples of vehicles and machinery that use drive shafts?
Drive shafts are widely used in various vehicles and machinery to transmit power from the engine or power source to the wheels or driven components. Here are some real-world examples of vehicles and machinery that utilize drive shafts:
1. Automobiles:
Drive shafts are commonly found in automobiles, especially those with rear-wheel drive or four-wheel drive systems. In these vehicles, the drive shaft transfers power from the transmission or transfer case to the rear differential or front differential, respectively. This allows the engine’s power to be distributed to the wheels, propelling the vehicle forward.
2. Trucks and Commercial Vehicles:
Drive shafts are essential components in trucks and commercial vehicles. They are used to transfer power from the transmission or transfer case to the rear axle or multiple axles in the case of heavy-duty trucks. Drive shafts in commercial vehicles are designed to handle higher torque loads and are often larger and more robust than those used in passenger cars.
3. Construction and Earthmoving Equipment:
Various types of construction and earthmoving equipment, such as excavators, loaders, bulldozers, and graders, rely on drive shafts for power transmission. These machines typically have complex drivetrain systems that use drive shafts to transfer power from the engine to the wheels or tracks, enabling them to perform heavy-duty tasks on construction sites or in mining operations.
4. Agricultural Machinery:
Agricultural machinery, including tractors, combines, and harvesters, utilize drive shafts to transmit power from the engine to the wheels or driven components. Drive shafts in agricultural machinery are often subjected to demanding conditions and may have additional features such as telescopic sections to accommodate variable distances between components.
5. Industrial Machinery:
Industrial machinery, such as manufacturing equipment, generators, pumps, and compressors, often incorporate drive shafts in their power transmission systems. These drive shafts transfer power from electric motors, engines, or other power sources to various driven components, enabling the machinery to perform specific tasks in industrial settings.
6. Marine Vessels:
In marine applications, drive shafts are commonly used to transmit power from the engine to the propeller in boats, ships, and other watercraft. Marine drive shafts are typically longer and designed to withstand the unique challenges posed by water environments, including corrosion resistance and appropriate sealing mechanisms.
7. Recreational Vehicles (RVs) and Motorhomes:
RVs and motorhomes often employ drive shafts as part of their drivetrain systems. These drive shafts transfer power from the transmission to the rear axle, allowing the vehicle to move and providing propulsion. Drive shafts in RVs may have additional features such as dampers or vibration-reducing components to enhance comfort during travel.
8. Off-Road and Racing Vehicles:
Off-road vehicles, such as SUVs, trucks, and all-terrain vehicles (ATVs), as well as racing vehicles, frequently utilize drive shafts. These drive shafts are designed to withstand the rigors of off-road conditions or high-performance racing, transmitting power efficiently to the wheels and ensuring optimal traction and performance.
9. Railway Rolling Stock:
In railway systems, drive shafts are employed in locomotives and some types of rolling stock. They transfer power from the locomotive’s engine to the wheels or propulsion system, enabling the train to move along the tracks. Railway drive shafts are typically much longer and may have additional features to accommodate the articulated or flexible nature of some train configurations.
10. Wind Turbines:
Large-scale wind turbines used for generating electricity incorporate drive shafts in their power transmission systems. The drive shafts transfer rotational energy from the turbine’s blades to the generator, where it is converted into electrical power. Drive shafts in wind turbines are designed to handle the significant torque and rotational forces generated by the wind.
These examples demonstrate the broad range of vehicles and machinery that rely on drive shafts for efficient power transmission and propulsion. Drive shafts are essential components in various industries, enabling the transfer of power from the source to the driven components, ultimately facilitating movement, operation, or the performance of specific tasks.

Are there variations in drive shaft designs for different types of machinery?
Yes, there are variations in drive shaft designs to cater to the specific requirements of different types of machinery. The design of a drive shaft is influenced by factors such as the application, power transmission needs, space limitations, operating conditions, and the type of driven components. Here’s an explanation of how drive shaft designs can vary for different types of machinery:
1. Automotive Applications:
In the automotive industry, drive shaft designs can vary depending on the vehicle’s configuration. Rear-wheel-drive vehicles typically use a single-piece or two-piece drive shaft, which connects the transmission or transfer case to the rear differential. Front-wheel-drive vehicles often use a different design, employing a drive shaft that combines with the constant velocity (CV) joints to transmit power to the front wheels. All-wheel-drive vehicles may have multiple drive shafts to distribute power to all wheels. The length, diameter, material, and joint types can differ based on the vehicle’s layout and torque requirements.
2. Industrial Machinery:
Drive shaft designs for industrial machinery depend on the specific application and power transmission requirements. In manufacturing machinery, such as conveyors, presses, and rotating equipment, drive shafts are designed to transfer power efficiently within the machine. They may incorporate flexible joints or use a splined or keyed connection to accommodate misalignment or allow for easy disassembly. The dimensions, materials, and reinforcement of the drive shaft are selected based on the torque, speed, and operating conditions of the machinery.
3. Agriculture and Farming:
Agricultural machinery, such as tractors, combines, and harvesters, often requires drive shafts that can handle high torque loads and varying operating angles. These drive shafts are designed to transmit power from the engine to attachments and implements, such as mowers, balers, tillers, and harvesters. They may incorporate telescopic sections to accommodate adjustable lengths, flexible joints to compensate for misalignment during operation, and protective shielding to prevent entanglement with crops or debris.
4. Construction and Heavy Equipment:
Construction and heavy equipment, including excavators, loaders, bulldozers, and cranes, require robust drive shaft designs capable of transmitting power in demanding conditions. These drive shafts often have larger diameters and thicker walls to handle high torque loads. They may incorporate universal joints or CV joints to accommodate operating angles and absorb shocks and vibrations. Drive shafts in this category may also have additional reinforcements to withstand the harsh environments and heavy-duty applications associated with construction and excavation.
5. Marine and Maritime Applications:
Drive shaft designs for marine applications are specifically engineered to withstand the corrosive effects of seawater and the high torque loads encountered in marine propulsion systems. Marine drive shafts are typically made from stainless steel or other corrosion-resistant materials. They may incorporate flexible couplings or dampening devices to reduce vibration and mitigate the effects of misalignment. The design of marine drive shafts also considers factors such as shaft length, diameter, and support bearings to ensure reliable power transmission in marine vessels.
6. Mining and Extraction Equipment:
In the mining industry, drive shafts are used in heavy machinery and equipment such as mining trucks, excavators, and drilling rigs. These drive shafts need to withstand extremely high torque loads and harsh operating conditions. Drive shaft designs for mining applications often feature larger diameters, thicker walls, and specialized materials such as alloy steel or composite materials. They may incorporate universal joints or CV joints to handle operating angles, and they are designed to be resistant to abrasion and wear.
These examples highlight the variations in drive shaft designs for different types of machinery. The design considerations take into account factors such as power requirements, operating conditions, space constraints, alignment needs, and the specific demands of the machinery or industry. By tailoring the drive shaft design to the unique requirements of each application, optimal power transmission efficiency and reliability can be achieved.


editor by CX 2024-05-15
China supplier Widely Used Pto Cardan Shaft with Shear Bolt Torque Limiter Triangular Tube Shaft Agricultural Tractor Pto Drive Shaft
Product Description
Transmission Shaft PTO Shaft for agricultural machine
Durable Transmission Shaft Made of aluminum alloy with excellent quality and carefully selected materials,the hot head greatly extends its service life.
Application Scope for PTO Shafts
Various types of agricultural machinery transmission shafts, with a wide range of product uses, which are mainly suitable for agricultural tractors,micro tillers,rotary tillers,seeders,fertilizer spreaders,lawn mowers,baling machines,grass bales and so on.
| Series | D(mm) | W(mm) | 540 | 1000 | ||||
| CV | KW | NM | CV | KW | NM | |||
| 1S | 22.0 | 54.0 | 16 | 12 | 210 | 25 | 18 | 172 |
| 2S | 23.8 | 61.3 | 21 | 15 | 270 | 31 | 23 | 220 |
| 3S | 27.0 | 70.0 | 30 | 22 | 390 | 47 | 35 | 330 |
| 4S | 27.0 | 74.6 | 35 | 26 | 460 | 55 | 40 | 380 |
| 5S | 30.2 | 80.0 | 47 | 35 | 620 | 74 | 54 | 520 |
| 6S | 30.2 | 92.0 | 64 | 47 | 830 | 100 | 74 | 710 |
| 7S | 30.2 | 106.5 | 75 | 55 | 970 | 118 | 87 | 830 |
| 8S | 35.0 | 106.5 | 95 | 70 | 1240 | 150 | 110 | 1050 |
| 9S | 41.0 | 108.0 | 120 | 88 | 1560 | 190 | 140 | 1340 |
Company Profile
Shuoxin, Sure thing.
ZheJiang Shuoxin Machinery Manufacturing Co., Ltd has been in the agricultural machinery industry for more than 30 years, the product range covering spraying machines, fertilizer spreaders, manure spreaders, mowers, rakes, land levellers and so on. In the 30 years’ service for agriculture field, Shuoxin has grown into an enterprise that integrates multiple business modules such as Design, Manufacture, Service and Information Survey. Shuoxin agricultural machinery have done a important work to nutrition supply and plant diseases & insect pests control for crops such as wheat, cotton, corn, rice, orchards and vegetables. With the ISO System certificates and CE production certificates, Cooperating with Shuixin can guarantee the partners with advanced machine products, reduced labor cost, improved work efficiency and promoted product revenue.
Certifications
Product packaging
Iron Farme Packing
All the machines are fixed in the Iron Frame by steel wire, the Frame use the steel which is thicker than 3mm. Strong enough to carry and protect the machine.
Black plastic film will also protect the machine from rain and sun shine.
All the frames is welded according to the machine size, to make sure the minimum size and weight.
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| Type: | Shaft |
|---|---|
| Usage: | Tillage, Harvester, Planting and Fertilization |
| Material: | Iron |
| Power Source: | Tractor |
| Weight: | 6kg |
| After-sales Service: | Online Service |
| Customization: |
Available
| Customized Request |
|---|

How do drive shafts ensure efficient power transfer while maintaining balance?
Drive shafts employ various mechanisms to ensure efficient power transfer while maintaining balance. Efficient power transfer refers to the ability of the drive shaft to transmit rotational power from the source (such as an engine) to the driven components (such as wheels or machinery) with minimal energy loss. Balancing, on the other hand, involves minimizing vibrations and eliminating any uneven distribution of mass that can cause disturbances during operation. Here’s an explanation of how drive shafts achieve both efficient power transfer and balance:
1. Material Selection:
The material selection for drive shafts is crucial for maintaining balance and ensuring efficient power transfer. Drive shafts are commonly made from materials such as steel or aluminum alloys, chosen for their strength, stiffness, and durability. These materials have excellent dimensional stability and can withstand the torque loads encountered during operation. By using high-quality materials, drive shafts can minimize deformation, flexing, and imbalances that could compromise power transmission and generate vibrations.
2. Design Considerations:
The design of the drive shaft plays a significant role in both power transfer efficiency and balance. Drive shafts are engineered to have appropriate dimensions, including diameter and wall thickness, to handle the anticipated torque loads without excessive deflection or vibration. The design also considers factors such as the length of the drive shaft, the number and type of joints (such as universal joints or constant velocity joints), and the use of balancing weights. By carefully designing the drive shaft, manufacturers can achieve optimal power transfer efficiency while minimizing the potential for imbalance-induced vibrations.
3. Balancing Techniques:
Balance is crucial for drive shafts as any imbalance can cause vibrations, noise, and accelerated wear. To maintain balance, drive shafts undergo various balancing techniques during the manufacturing process. Static and dynamic balancing methods are employed to ensure that the mass distribution along the drive shaft is uniform. Static balancing involves adding counterweights at specific locations to offset any weight imbalances. Dynamic balancing is performed by spinning the drive shaft at high speeds and measuring any vibrations. If imbalances are detected, additional adjustments are made to achieve a balanced state. These balancing techniques help minimize vibrations and ensure smooth operation of the drive shaft.
4. Universal Joints and Constant Velocity Joints:
Drive shafts often incorporate universal joints (U-joints) or constant velocity (CV) joints to accommodate misalignment and maintain balance during operation. U-joints are flexible joints that allow for angular movement between shafts. They are typically used in applications where the drive shaft operates at varying angles. CV joints, on the other hand, are designed to maintain a constant velocity of rotation and are commonly used in front-wheel-drive vehicles. By incorporating these joints, drive shafts can compensate for misalignment, reduce stress on the shaft, and minimize vibrations that can negatively impact power transfer efficiency and balance.
5. Maintenance and Inspection:
Regular maintenance and inspection of drive shafts are essential for ensuring efficient power transfer and balance. Periodic checks for wear, damage, or misalignment can help identify any issues that may affect the drive shaft’s performance. Lubrication of the joints and proper tightening of fasteners are also critical for maintaining optimal operation. By adhering to recommended maintenance procedures, any imbalances or inefficiencies can be addressed promptly, ensuring continued efficient power transfer and balance.
In summary, drive shafts ensure efficient power transfer while maintaining balance through careful material selection, thoughtful design considerations, balancing techniques, and the incorporation of flexible joints. By optimizing these factors, drive shafts can transmit rotational power smoothly and reliably, minimizing energy losses and vibrations that can impact performance and longevity.

What safety precautions should be followed when working with drive shafts?
Working with drive shafts requires adherence to specific safety precautions to prevent accidents, injuries, and damage to equipment. Drive shafts are critical components of a vehicle or machinery’s driveline system and can pose hazards if not handled properly. Here’s a detailed explanation of the safety precautions that should be followed when working with drive shafts:
1. Personal Protective Equipment (PPE):
Always wear appropriate personal protective equipment when working with drive shafts. This may include safety goggles, gloves, steel-toed boots, and protective clothing. PPE helps protect against potential injuries from flying debris, sharp edges, or accidental contact with moving parts.
2. Lockout/Tagout Procedures:
Before working on a drive shaft, ensure that the power source is properly locked out and tagged out. This involves isolating the power supply, such as shutting off the engine or disconnecting the electrical power, and securing it with a lockout/tagout device. This prevents accidental engagement of the drive shaft while maintenance or repair work is being performed.
3. Vehicle or Equipment Support:
When working with drive shafts in vehicles or equipment, use proper support mechanisms to prevent unexpected movement. Securely block the vehicle’s wheels or utilize support stands to prevent the vehicle from rolling or shifting during drive shaft removal or installation. This helps maintain stability and reduces the risk of accidents.
4. Proper Lifting Techniques:
When handling heavy drive shafts, use proper lifting techniques to prevent strain or injuries. Lift with the help of a suitable lifting device, such as a hoist or jack, and ensure that the load is evenly distributed and securely attached. Avoid lifting heavy drive shafts manually or with improper lifting equipment, as this can lead to accidents and injuries.
5. Inspection and Maintenance:
Prior to working on a drive shaft, thoroughly inspect it for any signs of damage, wear, or misalignment. If any abnormalities are detected, consult a qualified technician or engineer before proceeding. Regular maintenance is also essential to ensure the drive shaft is in good working condition. Follow the manufacturer’s recommended maintenance schedule and procedures to minimize the risk of failures or malfunctions.
6. Proper Tools and Equipment:
Use appropriate tools and equipment specifically designed for working with drive shafts. Improper tools or makeshift solutions can lead to accidents or damage to the drive shaft. Ensure that tools are in good condition, properly sized, and suitable for the task at hand. Follow the manufacturer’s instructions and guidelines when using specialized tools or equipment.
7. Controlled Release of Stored Energy:
Some drive shafts, particularly those with torsional dampers or other energy-storing components, can store energy even when the power source is disconnected. Exercise caution when working on such drive shafts and ensure that the stored energy is safely released before disassembly or removal.
8. Training and Expertise:
Work on drive shafts should only be performed by individuals with the necessary training, knowledge, and expertise. If you are not familiar with drive shafts or lack the required skills, seek assistance from qualified technicians or professionals. Improper handling or installation of drive shafts can lead to accidents, damage, or compromised performance.
9. Follow Manufacturer’s Guidelines:
Always follow the manufacturer’s guidelines, instructions, and warnings specific to the drive shaft you are working with. These guidelines provide important information regarding installation, maintenance, and safety considerations. Deviating from the manufacturer’s recommendations may result in unsafe conditions or void warranty coverage.
10. Disposal of Old or Damaged Drive Shafts:
Dispose of old or damaged drive shafts in accordance with local regulations and environmental guidelines. Improper disposal can have negative environmental impacts and may violate legal requirements. Consult with local waste management authorities or recycling centers to ensure appropriate disposal methods are followed.
By following these safety precautions, individuals can minimize the risks associated with working with drive shafts and promote a safe working environment. It is crucial to prioritize personal safety, use proper equipment and techniques, and seek professional help when needed to ensure the proper handling and maintenance of drive shafts.

How do drive shafts handle variations in length and torque requirements?
Drive shafts are designed to handle variations in length and torque requirements in order to efficiently transmit rotational power. Here’s an explanation of how drive shafts address these variations:
Length Variations:
Drive shafts are available in different lengths to accommodate varying distances between the engine or power source and the driven components. They can be custom-made or purchased in standardized lengths, depending on the specific application. In situations where the distance between the engine and the driven components is longer, multiple drive shafts with appropriate couplings or universal joints can be used to bridge the gap. These additional drive shafts effectively extend the overall length of the power transmission system.
Additionally, some drive shafts are designed with telescopic sections. These sections can be extended or retracted, allowing for adjustments in length to accommodate different vehicle configurations or dynamic movements. Telescopic drive shafts are commonly used in applications where the distance between the engine and the driven components may change, such as in certain types of trucks, buses, and off-road vehicles.
Torque Requirements:
Drive shafts are engineered to handle varying torque requirements based on the power output of the engine or power source and the demands of the driven components. The torque transmitted through the drive shaft depends on factors such as the engine power, load conditions, and the resistance encountered by the driven components.
Manufacturers consider torque requirements when selecting the appropriate materials and dimensions for drive shafts. Drive shafts are typically made from high-strength materials, such as steel or aluminum alloys, to withstand the torque loads without deformation or failure. The diameter, wall thickness, and design of the drive shaft are carefully calculated to ensure it can handle the expected torque without excessive deflection or vibration.
In applications with high torque demands, such as heavy-duty trucks, industrial machinery, or performance vehicles, drive shafts may have additional reinforcements. These reinforcements can include thicker walls, cross-sectional shapes optimized for strength, or composite materials with superior torque-handling capabilities.
Furthermore, drive shafts often incorporate flexible joints, such as universal joints or constant velocity (CV) joints. These joints allow for angular misalignment and compensate for variations in the operating angles between the engine, transmission, and driven components. They also help absorb vibrations and shocks, reducing stress on the drive shaft and enhancing its torque-handling capacity.
In summary, drive shafts handle variations in length and torque requirements through customizable lengths, telescopic sections, appropriate materials and dimensions, and the inclusion of flexible joints. By carefully considering these factors, drive shafts can efficiently and reliably transmit power while accommodating the specific needs of different applications.


editor by CX 2024-05-15